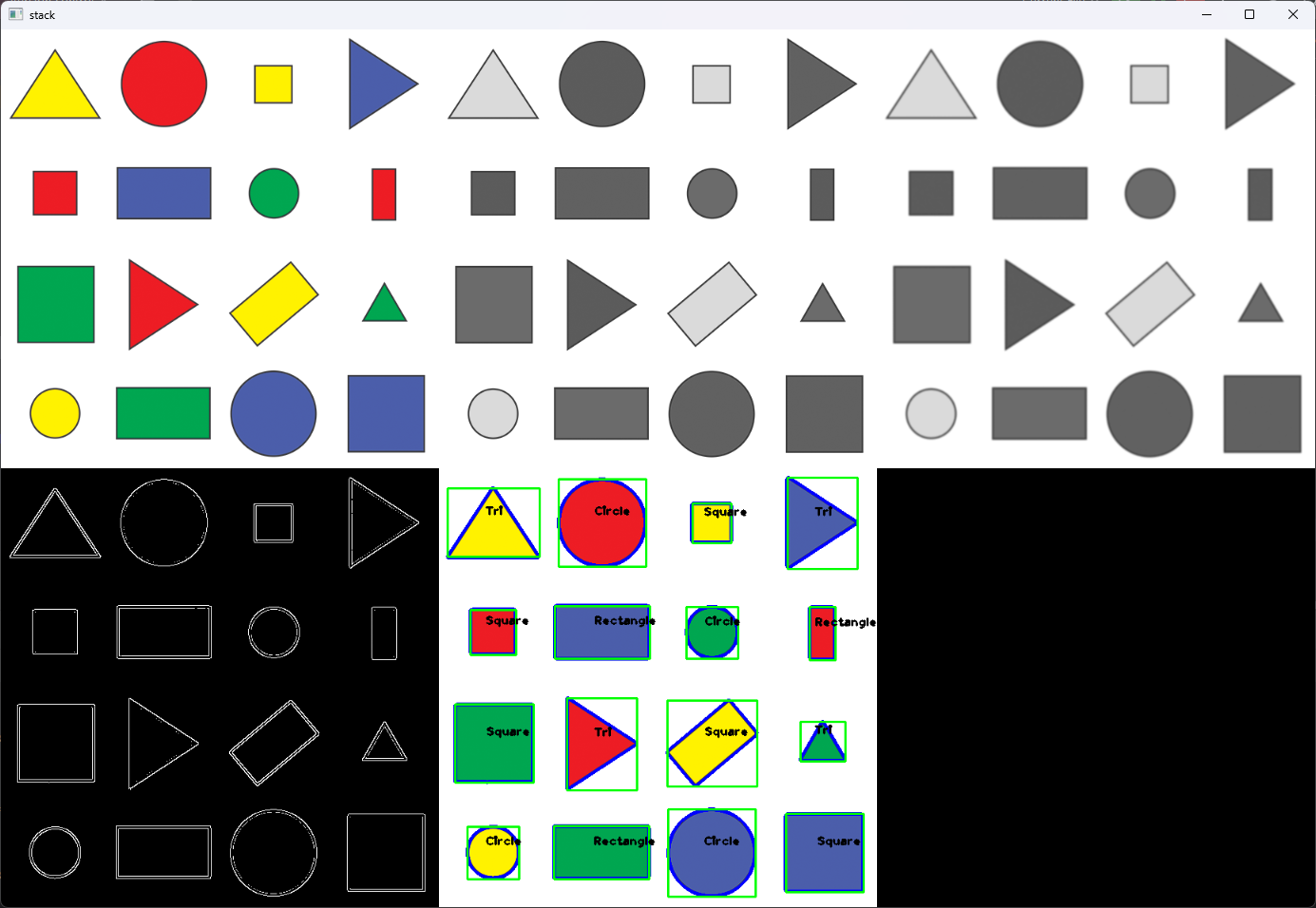
def getContours(img):contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)for cnt in contours:area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)print(area)if area > 500:# -1 代表所有的轮廓cv2.drawContours(imgContours, cnt, -1, (255, 0, 0), 3)# 找到轮廓的长度peri = cv2.arcLength(cnt, True)print(peri)# 会给出corner的坐标,polygonal是多边形approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, 0.02 * peri, True)# 3就是三角形、4是矩形,超过4就是圆形了print(len(approx))objCor = len(approx)# 置信框x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)if objCor == 3:ObjectType = "Tri"elif objCor == 4:aspRatio = w / float(h)if aspRatio > 0.95 and aspRatio < 1.1:ObjectType = "Square"else:ObjectType = "Rectangle"elif objCor >= 4:ObjectType = "Circle"else:ObjectType = "None"# 对角线,经常使用绿色的置信框,知道中心点cv2.rectangle(imgContours, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.putText(imgContours, ObjectType, (x + (w//2)-10, y + (h//2)-10),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, (0, 0, 0), 2)img = cv2.imread('images/shapes.png') imgContours = img.copy()imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) imgBlur = cv2.GaussianBlur(imgGray, (5, 5), 0) imgCanny = cv2.Canny(imgBlur, 50, 50) # 通过检测出来的边缘就可以去找轮廓的特征了 getContours(imgCanny)imgBlank = np.zeros_like(img) imgStack = stackImages(0.8, ([img, imgGray, imgBlur],[imgCanny, imgContours, imgBlank])) cv2.imshow('stack', imgStack)