问题背景
投产日,同事负责的项目新版本发布,版本包是SpringBoot v2.7.18的一个FatJar,java -jar启动报错停止了,输出的异常日志如下:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'dataSource' defined in class path resource [com/alibaba/druid/spring/boot/autoconfigure/DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure.class]: Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties$DataSourceBeanCreationException: Failed to determine a suitable driver class...省略Caused by: org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties$DataSourceBeanCreationException: Failed to determine a suitable driver classat org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties.determineDriverClassName(DataSourceProperties.java:186)at org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties.determineUsername(DataSourceProperties.java:280)at com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceWrapper.afterPropertiesSet(DruidDataSourceWrapper.java:40)...省略
版本回退,正好我也在旁边,记录下一起排查解决的过程。
定位与解决问题
分析错误日志
拉了版本分支代码,从下往上看输出的错误日志,发现是DruidDataSourceWrapper这个类中40行出错,看下这个类以及出错的位置:
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid")
class DruidDataSourceWrapper extends DruidDataSource implements InitializingBean {@Autowiredprivate DataSourceProperties basicProperties;@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {//if not found prefix 'spring.datasource.druid' jdbc properties ,'spring.datasource' prefix jdbc properties will be used.if (super.getUsername() == null) {// 关键行:这一行出错,basicProperties.determineUsername()这个方法会出现异常super.setUsername(basicProperties.determineUsername());}if (super.getPassword() == null) {super.setPassword(basicProperties.determinePassword());}if (super.getUrl() == null) {super.setUrl(basicProperties.determineUrl());}if (super.getDriverClassName() == null) {super.setDriverClassName(basicProperties.getDriverClassName());}}...
DruidDataSourceWrapper归属于druid-spring-boot-starter这个依赖,是 alibaba druid 数据库连接池的一个 starter。
结合错误日志看下basicProperties.determineUsername()这个方法里面出错的位置:
public String determineUsername() {if (StringUtils.hasText(this.username)) {return this.username;}// 关键行:调用determineDriverClassName()这个方法出错if (EmbeddedDatabaseConnection.isEmbedded(determineDriverClassName(), determineUrl())) {return "sa";}return null;
}
再次结合错误日志看下determineDriverClassName()这个方法里面出错的位置:
public String determineDriverClassName() {if (StringUtils.hasText(this.driverClassName)) {Assert.state(driverClassIsLoadable(), () -> "Cannot load driver class: " + this.driverClassName);return this.driverClassName;}String driverClassName = null;if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {driverClassName = DatabaseDriver.fromJdbcUrl(this.url).getDriverClassName();}if (!StringUtils.hasText(driverClassName)) {driverClassName = this.embeddedDatabaseConnection.getDriverClassName();}if (!StringUtils.hasText(driverClassName)) {// 关键行:在这边抛出的异常throw new DataSourceBeanCreationException("Failed to determine a suitable driver class", this,this.embeddedDatabaseConnection);}return driverClassName;
}
定位到了出错的位置,分析这块代码抛出异常的原因,意思就是如果spring.datasource.druid.username这个配置的值为空,那么读取spring.datasource.username这个配置,如果还是空,尝试从spring.datasource.url配置信息中解析jdbc驱动类,解析不出来就抛出DataSourceBeanCreationException异常。
版本变动点
是配置信息有问题?
问了下这个项目的配置原本是放在配置文件中的,公共配置放在了application.yml中,不同环境的配置采用application-{profile}.yml放置,如下:
application.yml
application-dev.yml
...
application-pro.yml
在application.yml中使用占位符借助 maven 打包时添加-P参数设置激活的profile:
spring:profiles:# envactive: @env@
项目 pom 文件中多个 profile 配置如下(这是本次版本的一个变动点):
<profiles><!-- DEV 开发环境--><profile><id>dev</id><properties><env>DEV</env>...</properties></profile>...<!-- PRO 生产环境--><profile><id>pro</id><properties><env>PRO</env>...</properties></profile>
</profiles>maven 打生产包,spring.profiles.active的值被设置成了PRO,也就是生产环境将使用application-PRO.yml这个配置文件。
这个版本的另一个变动点是接入了 apollo 配置中心,但是没有删除不同环境的配置文件,配置文件application.yml中增加了 apollo 相关的配置:
app:id: app-xxx-web
apollo:bootstrap:namespaces: applicationenabled: trueeagerLoad:enabled: true
分析 SpringBoot 的配置加载流程
触发时机
SpringBoot 应用启动时在 SpringApplication prepareEnvironment方法中发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener 中监听了这个事件触发配置信息读取,不同来源的配置信息有专门实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor接口的类进行处理,这些类实现postProcessEnvironment方法,apollo-client使用的是v1.9.0版本,其包含一个META-INF/spring.factories:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.ctrip.framework.apollo.spring.boot.ApolloAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
com.ctrip.framework.apollo.spring.boot.ApolloApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
com.ctrip.framework.apollo.spring.boot.ApolloApplicationContextInitializer
com.ctrip.framework.apollo.spring.boot.ApolloApplicationContextInitializer 会被扫描到,然后执行其postProcessEnvironment方法,多个EnvironmentPostProcessor的执行顺序由其内部的order属性决定,越小的越靠前,ApolloApplicationContextInitializer的order为0,属于是靠后的:
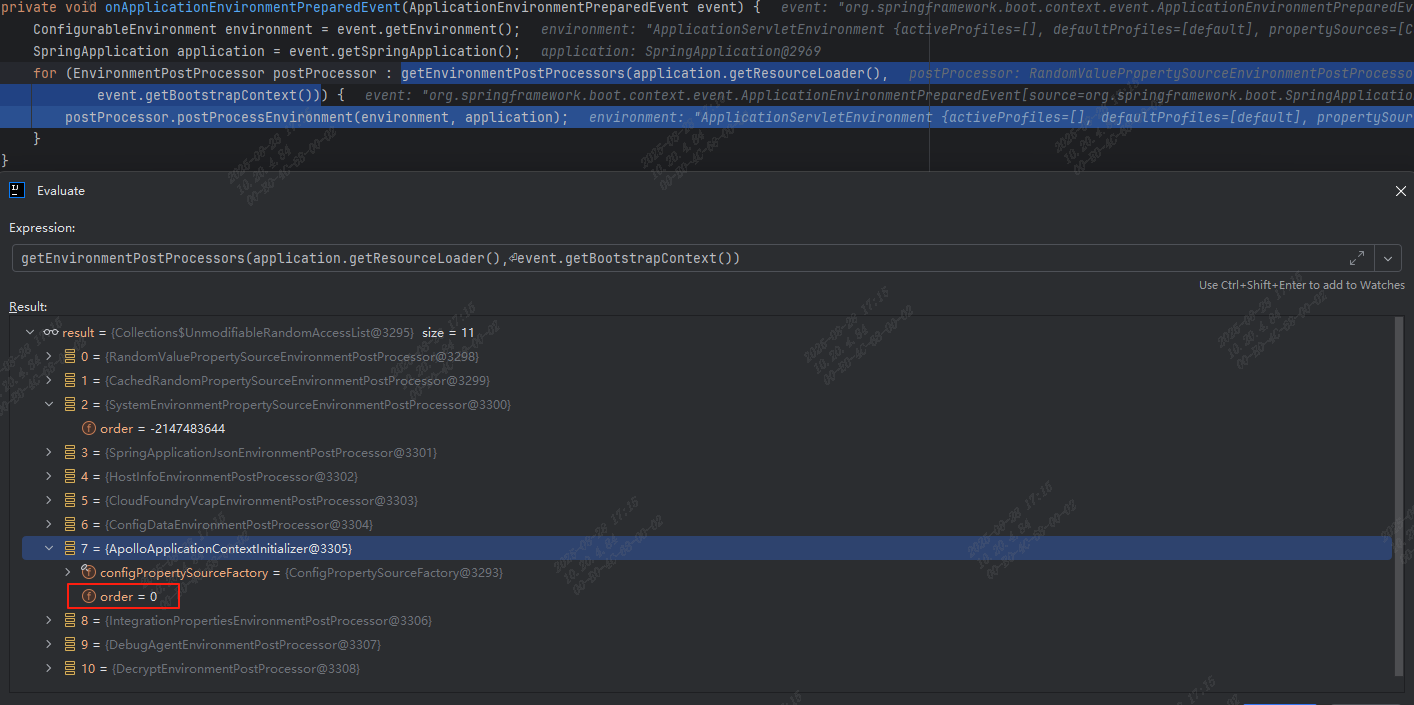
SpringBoot 中,后加载的属性源可以覆盖先加载的属性源定义的值,参考:属性源的优先级顺序,因此 apollo 中的配置会覆盖配置文件中的配置。
难道是 apollo 中的配置写错了?
看了下 apollo 中没有spring.datasource.url这个配置,数据库的连接信息是写在spring.datasource.druid这个前缀开头下面的,apollo 中有两个名为application的命名空间,一个格式是properties,另一个格式是yml,这些配置是写在yml格式命名空间下的,properties格式命名空间下的配置为空。
spring:# druid pooldatasource:druid:url: jdbc:mysql://...:3306/...?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&...username: ...password: ...driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Drivertype: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource...
idea 启动参数指定 apollo 配置,启动项目,本地 apollo 的缓存文件夹config-cache下是有配置文件存在的,不过只有一个文件app-xx-web+default+application.properties,里面是空的。
yml格式命名空间下的配置呢?
看了下 apollo 的文档,原来yml格式命名空间下的配置在客户端使用需要填写带后缀的完整名字。
注1:yaml/yml格式的namespace从1.3.0版本开始支持和Spring整合,注入时需要填写带后缀的完整名字,比如application.yml
注2:非properties、非yaml/yml格式(如xml,json等)的namespace暂不支持和Spring整合。
配置文件application.yml中修改apollo的配置,将namespaces从application修改为application.yml:
app:id: app-xxx-web
apollo:bootstrap:namespaces: application.ymlenabled: trueeagerLoad:enabled: true
本地调试启动ok,apollo 中的配置可以正常拉取,项目启动成功。
生产环境 apollo 中的配置没有生效的话,可application-{profile}.yml文件还在,应该还是能读取配置文件中的配置完成启动的吧?
额,不对, maven 打生产包,spring.profiles.active的值被设置成了PRO,但classpath下生产环境配置文件名称为 application-pro.yml,大小写不一致,能正常加载吗?
将application.yml配置文件中的app.apollo.bootstrap.namespaces配置还原,在 maven 的 Profiles 中勾选 dev ,spring.profiles.active的值被设置成了DEV,idea 中正常启动项目,说明 application-dev.yml这个配置文件被读取了。
拿生产包在本地java -jar启动,apollo 的配置服务器指定为dev环境,和生产环境报一样的错误:
java -Dapp.id=app-xxx-web -Dapollo.meta=http://10.100.x.x:8072 -jar app-xxx-web.jar
难道是 CICD 打包的问题?
没有加载的配置文件
本地打了一个包,启动也是报一样的错误,奇怪了,idea 里面启动和打成 FatJar 之后启动的行为还不一样。
idea 里面启动,spring.profiles.active 的值是大写的 DEV,application-dev.yml中的配置是能正常读取的,打成FatJar之后,spring.profiles.active的值是大写的 PRO,application-pro.yml中的配置却不能正常读取。
apollo 的 app.id 这个配置是放在application.yml中的,启动后本地 apollo 的配置缓存文件夹 config-cache 下是有配置的,说明 application.yml 是生效的,只是不同环境 application-{profile}.yml 文件中的配置没有生效。
得着重看看 SpringBoot 中读取配置文件的逻辑了。
配置文件的加载流程
上面分析到,EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener 中监听了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件做配置信息读取动作,不同来源的配置信息有专门实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor接口的类进行处理,配置文件的处理类是哪一个?
debug 看了下,是 ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,其 postProcessEnvironment 方法里面进行处理,然后调用了ConfigDataEnvironment类中的 processAndApply 方法,其内部会调用processWithProfiles方法:
private ConfigDataEnvironmentContributors processWithProfiles(ConfigDataEnvironmentContributors contributors,ConfigDataImporter importer, ConfigDataActivationContext activationContext) {this.logger.trace("Processing config data environment contributors with profile activation context");// 在这~~~contributors = contributors.withProcessedImports(importer, activationContext);registerBootstrapBinder(contributors, activationContext, ALLOW_INACTIVE_BINDING);return contributors;
}
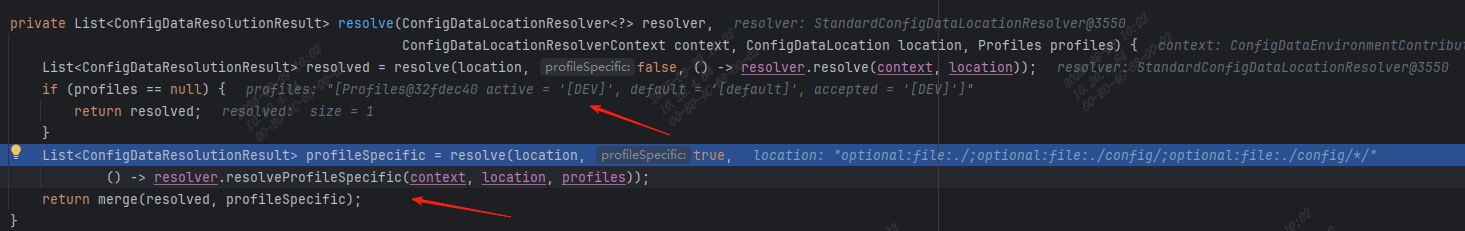
此时的contributors是ConfigDataEnvironmentContributors,继续跟踪 withProcessedImports 方法,里面会调用是ConfigDataImporter的 resolveAndLoad 方法:
/*** Resolve and load the given list of locations, filtering any that have been* previously loaded.* @param activationContext the activation context* @param locationResolverContext the location resolver context* @param loaderContext the loader context* @param locations the locations to resolve* @return a map of the loaded locations and data*/
Map<ConfigDataResolutionResult, ConfigData> resolveAndLoad(ConfigDataActivationContext activationContext,ConfigDataLocationResolverContext locationResolverContext, ConfigDataLoaderContext loaderContext,List<ConfigDataLocation> locations) {try {// 关键行:定位出使用的环境profileProfiles profiles = (activationContext != null) ? activationContext.getProfiles() : null;// 关键行:根据profile列出需要查找的配置文件列表List<ConfigDataResolutionResult> resolved = resolve(locationResolverContext, profiles, locations);return load(loaderContext, resolved);}catch (IOException ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("IO error on loading imports from " + locations, ex);}
}
因为我本地 debug 的时候 profile 指定的 dev,所以spring.profiles.active的值被设置成了DEV:
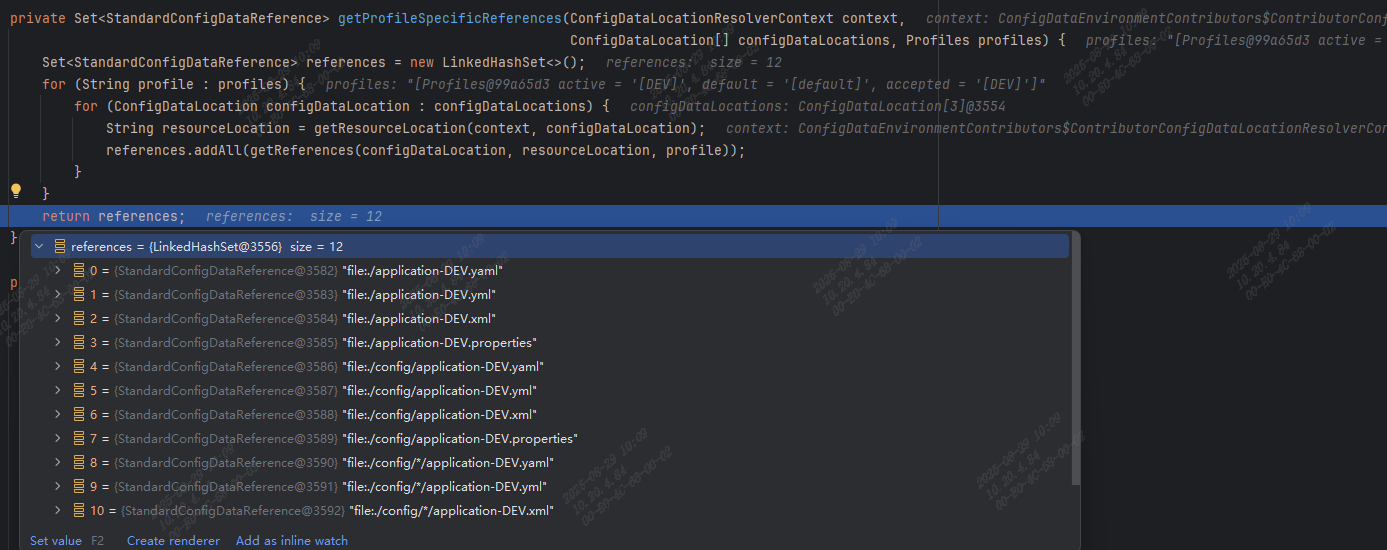
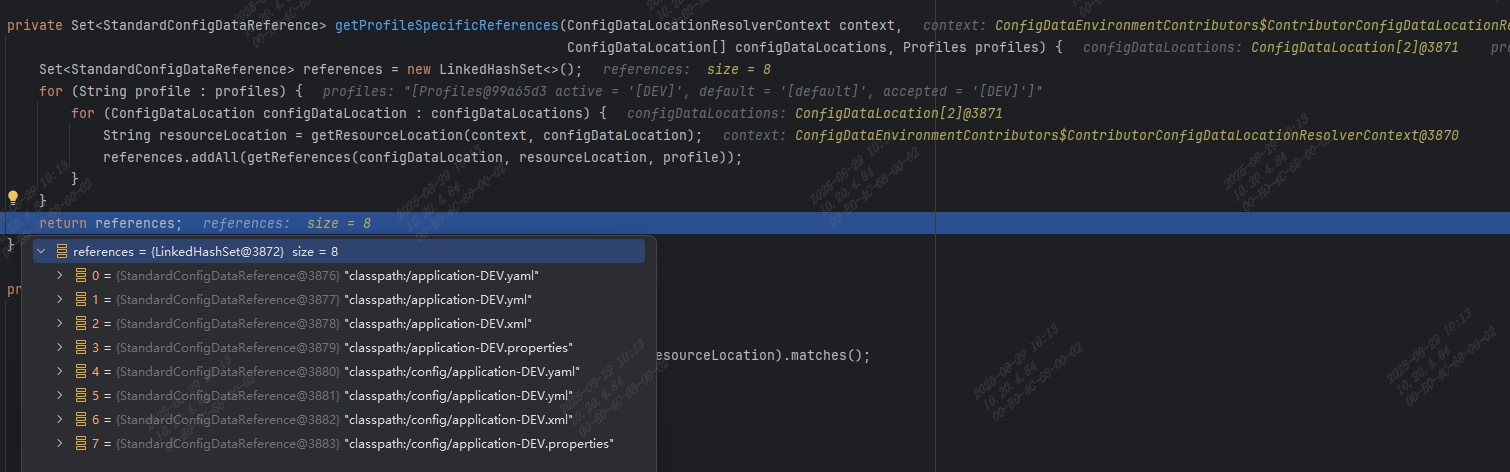
继续断点,跟踪到了StandardConfigDataLocationResolver类,其 getProfileSpecificReferences 方法中根据 profile 列出需要读取的配置文件路径列表:
继续断点到了获取配置文件资源的位置,是 resolveNonPattern 方法:
private List<StandardConfigDataResource> resolveNonPattern(StandardConfigDataReference reference) {// 关键行:通过统一的 ResourceLoader 接口获取资源Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(reference.getResourceLocation());// 关键行:调用 Resource.exists() 方法,如果文件存在,则继续在后面读取,否则忽略if (!resource.exists() && reference.isSkippable()) {logSkippingResource(reference);return Collections.emptyList();}return Collections.singletonList(createConfigResourceLocation(reference, resource));
}
因为 application-DEV.yml 是放在classpath下,在这加一个条件断点,只关注application-DEV.yml:
reference.getResourceLocation().equals("classpath:/application-DEV.yml");
判断文件是否存在这个语句执行的结果是存在的:
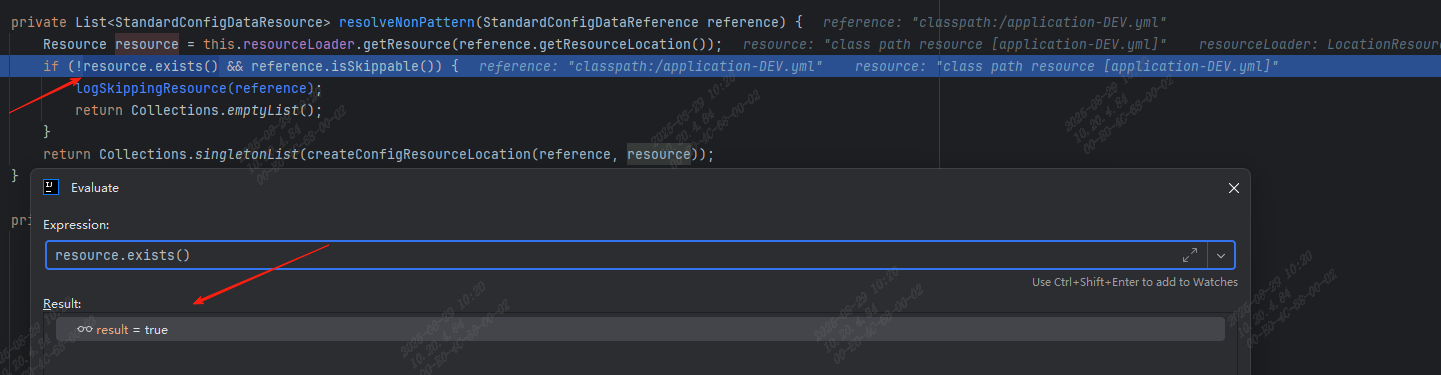
可见spring.profiles.active的值被设置成了DEV,本地在 idea 中 debug 项目代码也能正常加载 application-dev.yml ,会不会是打成 jar 包之后就不行呢?
远程调试生产包
idea 支持** Remote JVM Debug** ,我想要观测下生产版本 jar 包启动的时候,spring.profiles.active的值被设置成了PRO,这块代码判断 classpath:/application-PRO.yml 文件是否存在的结果。
在生产 jar 包目录下打开命令行窗口,执行以下命令,其中 suspend 需要设置成 y,代表回车执行命令需要等到 idea 连接到这个 5005 调试端口之后才继续执行程序:
java -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=5005 -Dapollo.meta=http://10.100.x.xx:8072 -jar app-xxx-web.jar --logging.level.root=TRACE
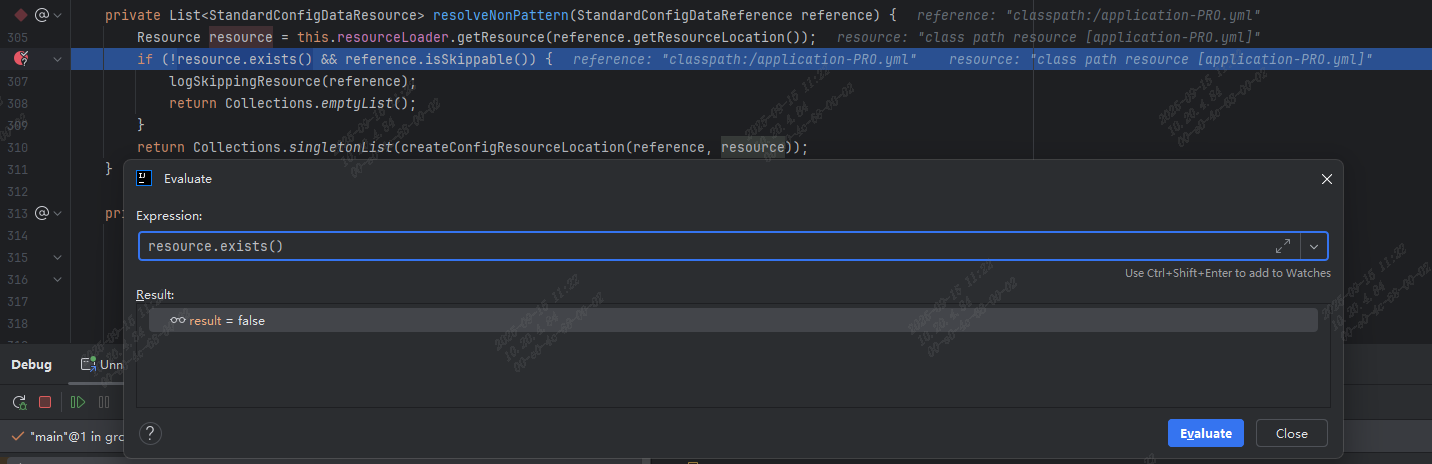
因为是生产包,所以需要改下条件断点为:
reference.getResourceLocation().equals("classpath:/application-PRO.yml");
Remote JVM Debug 启动后 , 判断 classpath:/application-PRO.yml 文件是否存在的结果为false,和 debug 项目代码不一样了:
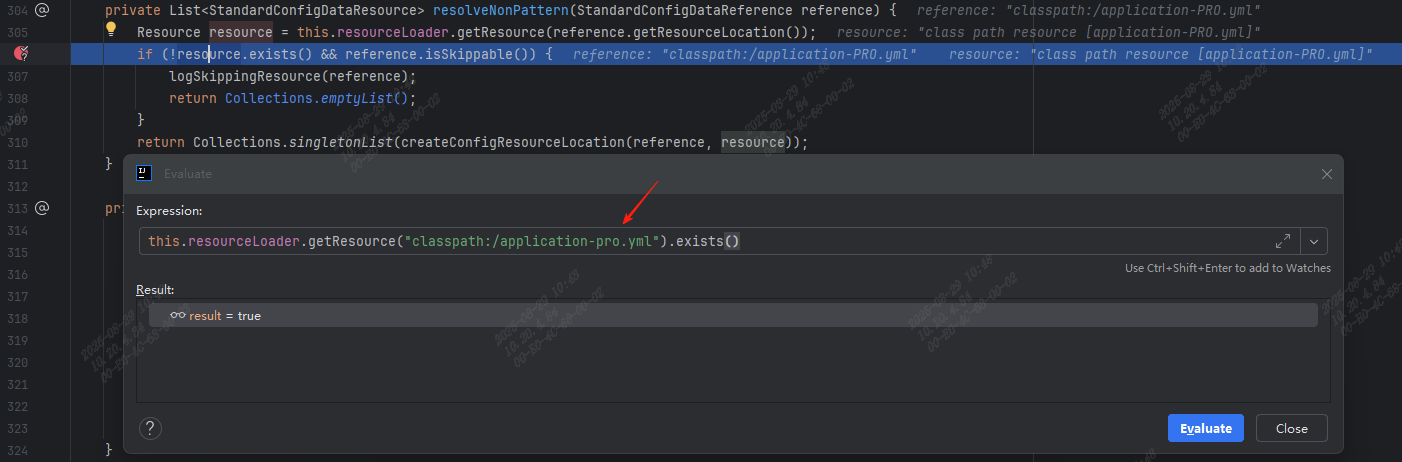
改成 classpath:/application-pro.yml 呢?在断点处执行以下命令,判断结果为 true了:
解决方案
分析到这,问题点和解决方案已经出来了:
- 项目 pom 文件中 profile 设置的 env 参数值本该小写但是用了大写
- 全面使用 apollo,去掉不同环境的配置文件,修正 apollo 命名空间配置为: apollo.bootstrap.namespaces = application.yml
可为什么测试环境没有出现这个问题呢,原来测试环境的启动脚本中指定了spring.profiles.active的值且是小写,生产环境启动脚本却没有指定。
🙂
深入认识 ClassLoader
不一样的 ClassLoader
版本能正常投产了,但是同一份代码不同的启动方式却有不同的表现,这着实让我费解,想着空余花点时间来弄明白这其中的原理。
resolveNonPattern 这个方法里面调用了resource.exists()方法判断配置文件是否存在,resource 是 spring-core 提供的 org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource 类:
/*** {@link Resource} implementation for class path resources. Uses either a* given {@link ClassLoader} or a given {@link Class} for loading resources.** <p>Supports resolution as {@code java.io.File} if the class path* resource resides in the file system, but not for resources in a JAR.* Always supports resolution as {@code java.net.URL}.** ...*/
public class ClassPathResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource {private final String path;@Nullableprivate ClassLoader classLoader;@Nullableprivate Class<?> clazz;/*** This implementation checks for the resolution of a resource URL.* @see ClassLoader#getResource(String)* @see Class#getResource(String)*/@Overridepublic boolean exists() {return (resolveURL() != null);}/*** Resolves a URL for the underlying class path resource.* @return the resolved URL, or {@code null} if not resolvable*/@Nullableprotected URL resolveURL() {try {if (this.clazz != null) {return this.clazz.getResource(this.path);}else if (this.classLoader != null) {// 关键行:委托给具体的 ClassLoaderreturn this.classLoader.getResource(this.path);}else {return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(this.path);}}catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {// Should not happen according to the JDK's contract:// see https://github.com/openjdk/jdk/pull/2662return null;}}...
}
2.7.18 版本的 SpringBoot 使用的 spring-core 版本为 5.3.31,exists() 方法会调用本类中的 resolveURL() 方法,debug 看了下,不管是 idea 启动还是打成 jar 之后启动,resolveURL 方法中都是通过return this.classLoader.getResource(this.path)返回配置文件的 URL 的,区别在于:
- idea 中启动时,
classLoader为Launcher$AppClassLoader,exists方法中return (resolveURL() != null)的返回值为 true - 打成 jar 之后启动,
classLoader为LaunchedURLClassLoader,exists方法中return (resolveURL() != null)的返回值为 false
Launcher$AppClassLoader 与 LaunchedURLClassLoader 的差异
类加载器的架构差异
Launcher$AppClassLoader 是 JDK 标准的三层类加载器架构中的系统类加载器:
// JDK 类加载器层次结构
Bootstrap ClassLoader (C++实现,加载JRE核心类)↓
Extension ClassLoader (加载JRE扩展包)↓
AppClassLoader (系统类加载器,加载-classpath指定路径)
在 idea 环境中运行时,应用类路径由 idea 动态构建,通常包含:
项目编译输出目录(如target/classes)
所有依赖的 JAR 文件
idea 特定的资源目录
此时的资源查找基于文件系统,ClassLoader.getResource()方法会遍历类路径中的每个条目,在文件系统上直接查找对应的资源文件。
LaunchedURLClassLoader 是 SpringBoot 为 FatJar 设计的特殊类加载器:
// SpringBoot FatJar 类加载架构
LaunchedURLClassLoader↓
URLClassLoader↓
ClassLoader (父类加载器)
其特殊之处在于能够处理"嵌套的JAR"(nested JARs)——即 FatJar 中内嵌的其他 JAR 文件。
资源解析机制的对比
AppClassLoader 的资源解析流程:
// 简化版的资源查找逻辑
public URL getResource(String name) {URL url;// 首先委托父加载器查找if (parent != null) {url = parent.getResource(name);} else {url = getBootstrapResource(name);}if (url == null) {// 在自身的类路径中查找url = findResource(name);}return url;
}
// 在文件系统中的查找
URL findResource(String name) {for (File classpathEntry : classpath) {File resourceFile = new File(classpathEntry, name);if (resourceFile.exists()) {return resourceFile.toURI().toURL();}}return null;
}
关键特性:
基于文件系统路径直接查找
受操作系统文件系统大小写规则影响(Windows 不敏感,Linux 敏感)
支持通配符和模式匹配
LaunchedURLClassLoader 的资源解析流程:
// SpringBoot 自定义的资源查找
public URL findResource(String name) {// 1. 首先尝试从已索引的资源中查找URL url = findResourceFromIndex(name);if (url != null) {return url; }// 2. 在嵌套的JAR文件中查找for (JarFile jar : nestedJars) {JarEntry entry = jar.getJarEntry(name);if (entry != null) {try {// 创建特殊的URL指向JAR内的资源return createJarUrl(jar, entry);} catch (IOException e) {// 处理异常}}}// 3. 回退到标准的URLClassLoader查找return super.findResource(name);
}
关键特性:
基于 JAR 文件条目的精确匹配
严格的大小写敏感性(ZIP/JAR实现的实际要求)
需要预先构建资源索引以提高性能
FatJar 中的资源定位机制
SpringBoot FatJar 的特殊结构:
app.jar
├── META-INF/
├── BOOT-INF/
│ ├── classes/ # 应用类文件
│ │ └── application.yml
│ └── lib/ # 依赖库
│ ├── spring-core.jar
│ └── druid.jar
└── org/springframework/boot/loader/├── Launcher.class└── LaunchedURLClassLoader.class
资源解析的核心挑战:
- JAR 规范的限制:
- JAR 文件本质上是 ZIP 文件
- 严格的大小写敏感性(ZIP/JAR实现的实际要求),
application-PRO.yml≠application-pro.yml
SpringBoot 的优化策略:
// SpringBoot 在构建时创建资源索引
private Map<String, List<String>> createResourceIndex() {Map<String, List<String>> index = new HashMap<>();for (JarFile jar : getAllJars()) {Enumeration<JarEntry> entries = jar.entries();while (entries.hasMoreElements()) {JarEntry entry = entries.nextElement();if (!entry.isDirectory()) {String path = entry.getName();// 将路径转换为标准形式String normalized = normalizePath(path);index.computeIfAbsent(normalized, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(path);}}}return index;
}
- 类加载器的初始化差异:
- idea 环境:类路径包含具体的目录和文件
- FatJar 环境:类路径指向 JAR 文件内部的嵌套结构
操作系统的影响
开发环境(Windows):
// 文件系统级别的大小写处理
File file = new File("application-PRO.yml");
System.out.println(file.exists());
// Windows: 如果存在application-pro.yml,可能返回true(不敏感)
// Linux: 严格返回false(敏感)
生产环境(Linux):
// JAR文件内部的资源查找
JarFile jar = new JarFile("app.jar");
JarEntry entry1 = jar.getJarEntry("application-PRO.yml"); // null
JarEntry entry2 = jar.getJarEntry("application-pro.yml"); // 找到条目
SpringBoot 配置加载的完整链条
理解整个配置加载过程中 ClassLoader 的作用:
// 配置解析的完整调用链
ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor.postProcessEnvironment()→ ConfigDataEnvironment.processAndApply()→ ConfigDataImporter.resolveAndLoad()→ StandardConfigDataLocationResolver.resolve()→ ClassPathResource.exists()→ LaunchedURLClassLoader.getResource()→ JarFile.getJarEntry() // 严格大小写匹配
关键发现:
- 在 FatJar 中,资源查找最终委托给
java.util.jar.JarFile JarFile.getJarEntry()方法基于哈希表实现,要求精确的键匹配- 哈希键的计算基于原始字节,不进行大小写转换
问题复现的技术根源
通过源码分析,可以精确重现问题:
// 问题重现的伪代码
public class ProblemReproduction {public static void main(String[] args) {// 开发环境(IDE)ClassLoader devLoader = Launcher.AppClassLoader;URL devResource = devLoader.getResource("application-PRO.yml");System.out.println("DEV Found: " + (devResource != null)); // true// 生产环境(FatJar)ClassLoader prodLoader = new LaunchedURLClassLoader();URL prodResource = prodLoader.getResource("application-PRO.yml");System.out.println("PROD Found: " + (prodResource != null)); // false// 实际存在的文件URL actualResource = prodLoader.getResource("application-pro.yml");System.out.println("Actual Found: " + (actualResource != null)); // true}
}
设计启示与最佳实践
架构层面的启示:
- 环境一致性:开发、测试、生产环境的运行时行为应该尽可能一致
- 早期验证:在构建阶段就应该检测配置文件和类路径的一致性
- 防御性编程:对资源加载进行适当的容错处理
技术实践建议:
// 防御性的资源配置加载
public class SafeConfigLoader {public static Resource loadConfig(ClassLoader loader, String baseName, String profile) {// 尝试规范化的命名String[] possibleNames = {baseName + "-" + profile.toLowerCase() + ".yml",baseName + "-" + profile.toUpperCase() + ".yml",baseName + "-" + profile + ".yml"};for (String name : possibleNames) {Resource resource = loader.getResource(name);if (resource != null && resource.exists()) {return resource;}}return null;}
}
构建期检查:
<!-- Maven 构建期资源验证 -->
<plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-enforcer-plugin</artifactId><configuration><rules><requireFilesExist><files><!-- 验证配置文件命名一致性 --><file>src/main/resources/application-${env}.yml</file></files></requireFilesExist></rules></configuration>
</plugin>
