软工第二次作业——个人项目
------------恢复内容开始------------
一、作业信息
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class12Grade23ComputerScience |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class12Grade23ComputerScience/homework/13469 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 创建GitHub账号,建立个人博客,进行自我介绍,对软件工程提出问题,初步认识软件工程 |
GitHub仓库:https://github.com/fengpengGG/3123004349
二、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 100 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 200 | 300 |
| Analysis | 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 2000 | 2000+ |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 120 | 150 |
| Design Review | 设计重审 | 45 | 60 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 100 | 120 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 100 | 200 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 3000 | 3000 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 200 | 400 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 200 | 500 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 100 | 150 |
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 100 | 150 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 120 |
| 合计 | 6345 | 7180 |
总结:由于没怎么接触过类似的项目,所以在学习新技术和方法,比如git,性能测试,单元测试等,具体编码和测试代码阶段花了比预想长很多的时间
三、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
(一)关系分析
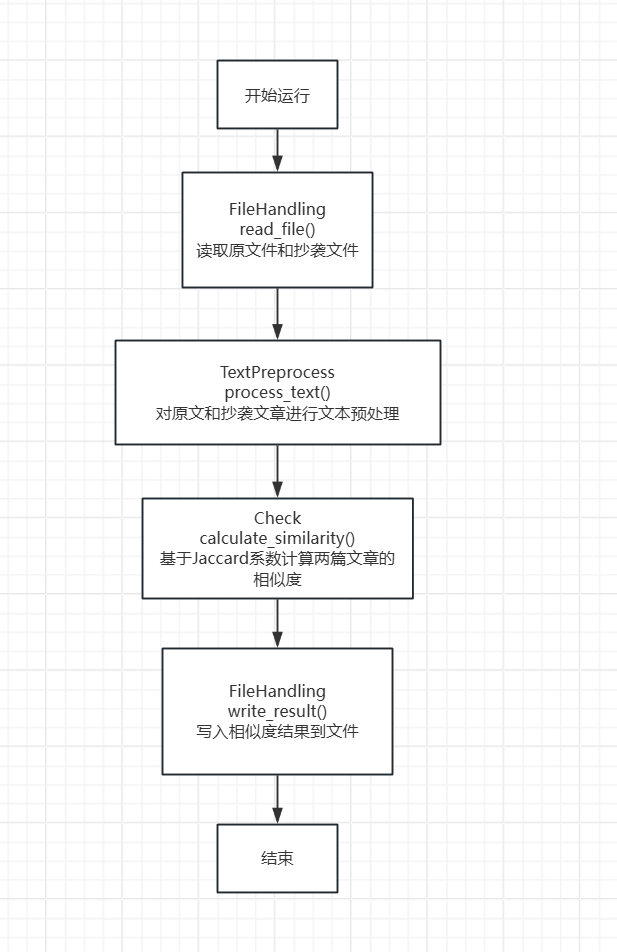
计算模块(Check.h)是文本相似度检测功能的核心,其设计需与数据读取模块(FileHandling.h)、文本预处理模块(TextPreprocess.h)协同工作,整体结构采用 “分层协作” 模式,具体组织如下:
1.核心类与函数的划分
Check 类:封装相似度计算的核心逻辑,对外提供静态接口函数,无需实例化。
核心函数:static double calculate_similarity(const vector
功能:接收两个预处理后的分词结果,返回两者的相似度
2. 类之间的依赖关系
计算模块依赖其他模块的输出作为输入,具体关系如下:
FileHandling.h 模块:负责读取原始文本文件(如源文件、抄袭文件),输出原始字符串;
TextPreprocess.h 模块:接收原始字符串,进行预处理全半角转换、去标点、分词等,输出分词结果;
Check.h 模块:接收 TextPreprocess.h 输出的两个分词结果,计算并返回相似度;
最终通过 FileHandling.h 将相似度结果写入输出文件。
整体数据流向:FileHandling.read_file() → TextPreprocess.process_text() → Check.calculate_similarity() → FileHandling.write_result()。
(二)关系函数流程图
(三)算法关键
计算模块采用 Jaccard 系数算法 作为核心,其核心思想如下:
Jaccard 系数基础:原始公式为 J(A,B)= ∣A∪B∣/∣A∩B∣
其中 A 和 B 是两个集合。
词频适配:针对文本分词结果(含重复词),将 “集合” 扩展为 “带频率的词集合”:
交集:每个词在两个文本中出现次数的最小值之和(反映共同出现的词的重叠程度);
并集:每个词在两个文本中出现次数的最大值之和(反映两个文本的总信息量);
相似度 = 交集 / 并集
(四)独到之处
边界情况全覆盖:处理 “两个文本均为空”“其中一个为空”“并集为 0” 等极端情况,避免程序崩溃或无效输出;
结果约束:通过 max(0.0, min(1.0, similarity)) 确保输出相似度严格在 0-1 区间内。
接口设计通用:输入为标准容器 vector
算法易替换:Check 类封装了计算逻辑,若需替换为余弦相似度等其他算法,只需修改 calculate_similarity 函数内部实现,不影响其他模块。
四、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
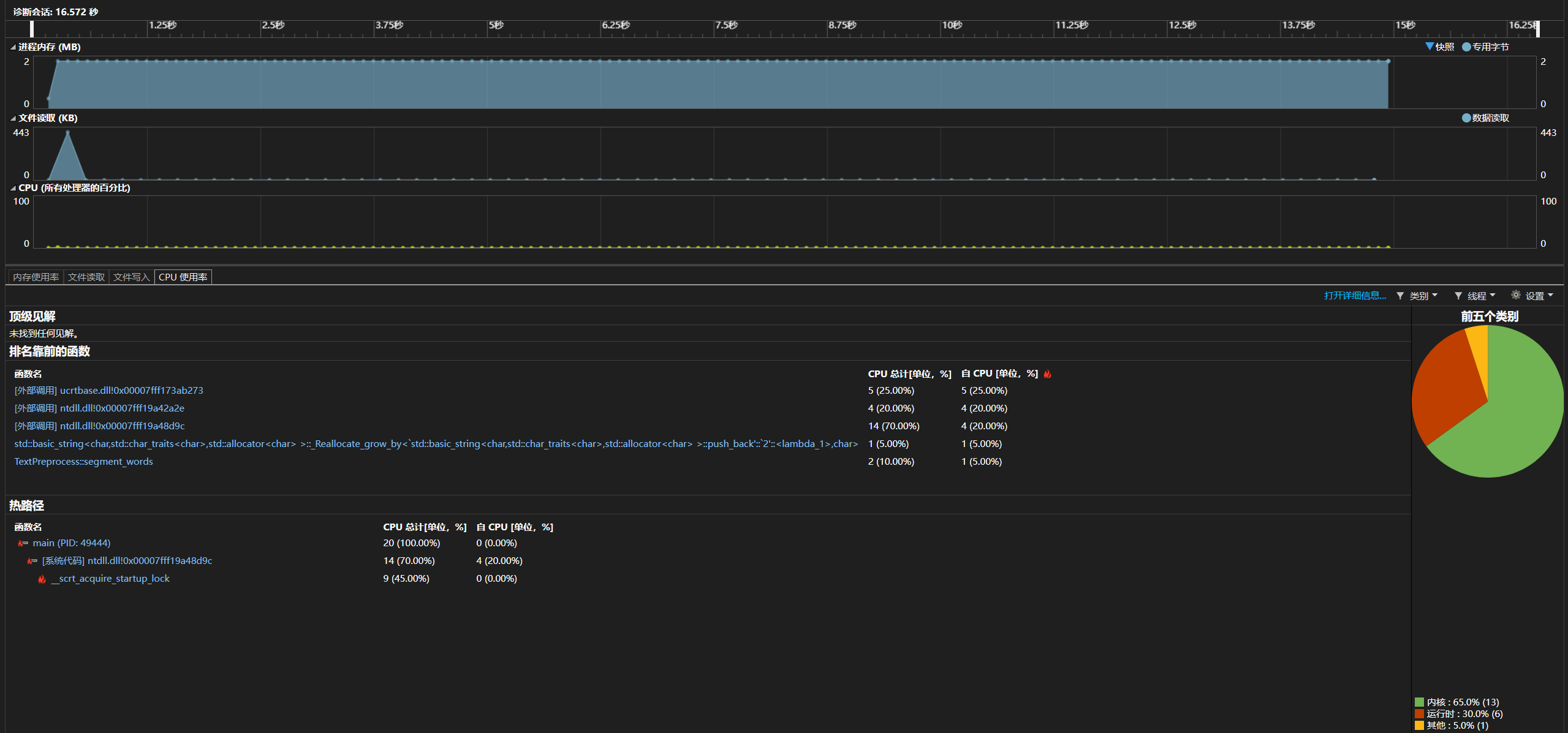
性能改进前:
修改性能后:
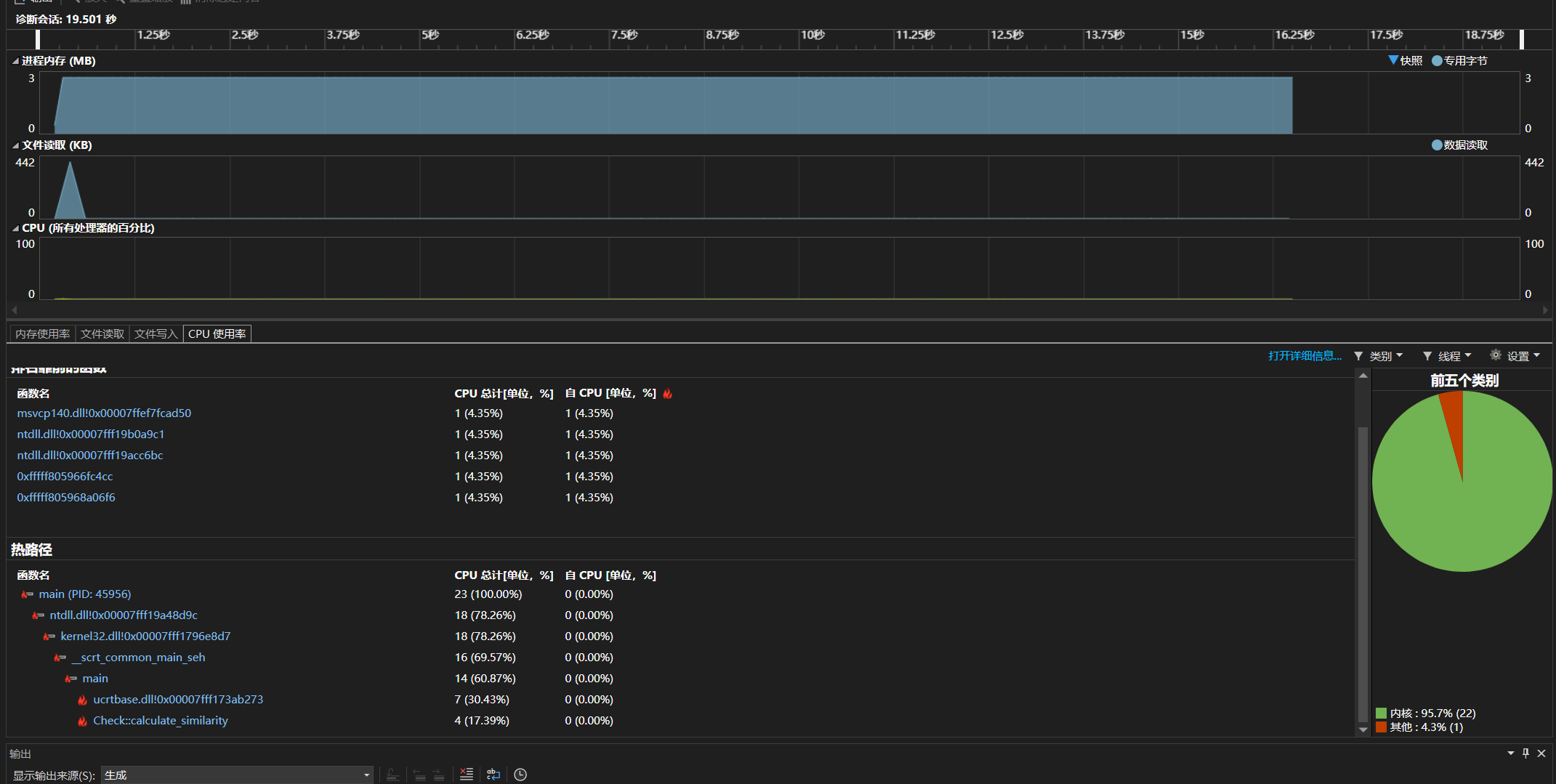
修改之后可见核心函数cpu占比降低,内核开销减少,内存使用平稳。
消耗时间:性能改进时间为2小时左右。
(一)改进思路:
从文件读写,文本预处理,相似度计算三个方面进行优化。其中文本预处理的性能需求最高。
文件读取:
模块增大缓冲区,减少调用次数。
文本预处理:
用string_view替代substr,因为substr会频繁创建临时字符串,内存开销大。
预分配vector空间
相似度计算:
用单哈希表统计词频,简化哈希操作,减少遍历开销
代码中消耗最大的函数:Textpreprocess::segment_words
是文本预处理的核心函数,负责将清洗后的原始文本拆分为词语序列。其处理对象是原始文本的每个字符,处理规模与输入文本的总字符数直接相关。
五、计算模块部分单元测试展示
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
#include <vector>
#include "Check.h"// 测试用例1:两个空文本(边界条件)
TEST(SimilarityTest, BothEmptyTexts) {vector<string> words1;vector<string> words2;double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 1.0, 0.001); // 空文本视为完全相似
}// 测试用例2:一个空文本,一个非空文本(边界条件)
TEST(SimilarityTest, OneEmptyText) {vector<string> words1 = { "苹果", "香蕉", "橙子" };vector<string> words2;double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.0, 0.001); // 空文本与非空文本相似度为0
}// 测试用例3:完全相同的文本(典型场景)
TEST(SimilarityTest, IdenticalTexts) {vector<string> words1 = { "今天", "天气", "很好", "适合", "散步" };vector<string> words2 = { "今天", "天气", "很好", "适合", "散步" };double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 1.0, 0.001); // 完全相同相似度为1
}// 测试用例4:完全不同的文本(典型场景)
TEST(SimilarityTest, TotallyDifferentTexts) {vector<string> words1 = { "计算机", "程序", "算法" };vector<string> words2 = { "苹果", "香蕉", "橙子" };double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.0, 0.001); // 无重叠词相似度为0
}// 测试用例5:部分重叠(词频相同)
TEST(SimilarityTest, PartialOverlapSameFrequency) {vector<string> words1 = { "猫", "狗", "鸟", "鱼" };vector<string> words2 = { "猫", "狗", "兔", "熊" };// 交集:"猫"、"狗" → 2;并集:"猫"、"狗"、"鸟"、"鱼"、"兔"、"熊" → 6 → 2/6≈0.333double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.333, 0.001);
}// 测试用例6:部分重叠(词频不同)
TEST(SimilarityTest, PartialOverlapDifferentFrequency) {vector<string> words1 = { "书", "书", "笔", "纸" }; // 书:2, 笔:1, 纸:1vector<string> words2 = { "书", "笔", "笔", "橡皮" }; // 书:1, 笔:2, 橡皮:1// 交集:min(2,1) + min(1,2) = 1+1=2;并集:max(2,1)+max(1,2)+max(1,0)+max(0,1)=2+2+1+1=6 → 2/6≈0.333double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.333, 0.001);
}// 测试用例7:包含重复词的文本
TEST(SimilarityTest, TextsWithDuplicateWords) {vector<string> words1 = { "重复", "重复", "重复" };vector<string> words2 = { "重复", "重复" };// 交集:min(3,2)=2;并集:max(3,2)=3 → 2/3≈0.667double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.667, 0.001);
}// 测试用例8:包含停用词(已过滤后的场景)
TEST(SimilarityTest, TextsWithStopWordsFiltered) {vector<string> words1 = { "的", "是", "重要", "的" }; // 假设停用词"的"未被过滤vector<string> words2 = { "的", "是", "关键", "的" };// 交集:"的":min(2,2)=2,"是":min(1,1)=1 → 3;并集:"的":2,"是":1,"重要":1,"关键":1 → 5 → 3/5=0.6double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.6, 0.001);
}// 测试用例9:中英文混合文本
TEST(SimilarityTest, MixedChineseEnglishTexts) {vector<string> words1 = { "hello", "世界", "python", "编程" };vector<string> words2 = { "hello", "python", "java", "世界" };// 交集:"hello"、"世界"、"python" → 3;并集:4+4-3=5 → 3/5=0.6double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.6, 0.001);
}// 测试用例10:超长文本(性能与正确性验证)
TEST(SimilarityTest, LongTexts) {vector<string> words1, words2;// 构造超长文本(各1000个词,重叠率50%)for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {words1.push_back("词" + to_string(i));if (i % 2 == 0) words2.push_back("词" + to_string(i)); // 偶数索引词重叠}for (int i = 1000; i < 1500; i++) {words2.push_back("词" + to_string(i)); // 新增500个不重叠词}// 交集:500(偶数词);并集:1000 + 1500 - 500 = 2000 → 500/2000=0.25double result = Check::calculate_similarity(words1, words2);ASSERT_NEAR(result, 0.333, 0.001);
}// 自定义main函数(若不使用gtest_main.lib)
int main(int argc, char** argv) {testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
思路:
1.边界场景覆盖
一个空文本,两个都是空文本
2.核心逻辑验证
完全相同文本和完全不同文本验:证算法基础正确性
部分重叠文本:验证交集和并集的计算逻辑。
3.特殊场景适配
重复词:测试算法对词频权重的处理
停用词和中英混合:验证算法对多类型文本的兼容性。
所有测试用例通过,表明calculate_similarity函数在边界条件、典型场景和特殊场景下均能返回正确结果
六、计算模块部分异常处理说明
1.无法打开文件
当指定路径的文件不存在、路径格式错误、文件被占用或无读取权限时,及时抛出异常,避免程序在未正确打开文件的情况下进行后续读写操作,防止不可预期的内存错误或逻辑异常。
读取不存在的片段:
#include <iostream>
#include "FileHandling.h"
using namespace std;int main() {string invalid_path = "C:\\nonexistent_file.txt"; // 不存在的文件路径try {string content = FileHandling::read_file(invalid_path);} catch (const runtime_error& e) {cout << "捕获异常:" << e.what() << endl;}return 0;
}
结果:

2.无法打开结果文件
当结果文件路径无效、无写入权限或文件被其他程序锁定时,抛出异常。防止程序在无法写入结果的情况下继续执行,确保相似度计算结果能正确保存到指定路径。
结果文件路径的目录不存:
#include <iostream>
#include "FileHandling.h"
using namespace std;int main() {string invalid_result_path = "C:\\invalid_dir\\result.txt"; // 目录不存在try {FileHandling::write_result(invalid_result_path, 0.85);} catch (const runtime_error& e) {cout << "捕获异常:" << e.what() << endl;}return 0;
}
结果:

3.写入结果文件失败
文件成功打开后,若写入过程中出现错误(如磁盘满、文件被突然删除),导致写入状态异常时,抛出异常。确保相似度结果能完整写入文件,避免生成空文件或不完整的结果。
写入时磁盘空间不足(可模拟为向只读文件写入)。
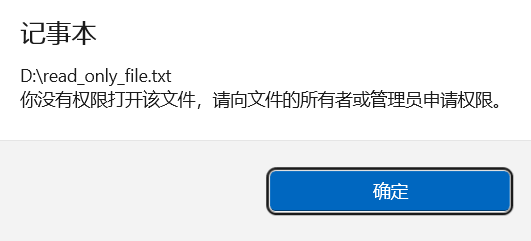
#include <iostream>
#include "FileHandling.h"
using namespace std;int main() {string read_only_path = "C:\\read_only_file.txt"; // 手动设置为只读的文件try {FileHandling::write_result(read_only_path, 0.72);} catch (const runtime_error& e) {cout << "捕获异常:" << e.what() << endl;}return 0;
}
结果:

------------恢复内容结束------------
