02020508 EF Core高级08-表达式树、Expression和委托的关系、查看表达式树结构、AST、手动创建表示树、工厂方法
1. 什么是表达式树:Expression和Func的区别(视频3-41)
1.1 表达式树的概念
1、表达式树(Expression Tree):树形数据结构表示代码,以表示逻辑运算,以便可以在运行时访问逻辑运算的结构。
2、Expression<TDelegate>类型
3、从Lambda表达式来生成表达式树:Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b =>b.Price > 5;
- 表达式树的理解比较难,如果学不懂不要有太大压力,这是装B用的。在实际开发中,前面讲到的EF Core知识点占用了90以上,表达式树用到的情况比较少。
1.2 了解EF Core的翻译SQL语句的机制
// EF Core中翻译为SQL示例
b.Name.Contains("杨") → where Name like "杨"
b =>b.Price > 5 → select * from books where price > 5;引入问题:EF Core怎么知道将C#表达式翻译为SQL语句?
答:通过编译原理知识,表达式树,节点等知识来实现,了解即可。
1.3 理解表达式树示例:迁移数据库
// Book.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace TreeDemo
{class Book{public long Id { get; set; } //主键public string Title { get; set; }//标题public DateTime PubTime { get; set; }//发布日期public double Price { get; set; }// 价格public string AuthorName { get; set; } // 新建属性(对应数据表中的行)}
}
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
// BookConfig.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders;namespace TreeDemo
{class BookConfig : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Book>{public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Book> builder){builder.ToTable("T_Books");builder.Property(e => e.Title).HasMaxLength(50).IsRequired();builder.Property(e => e.AuthorName).HasMaxLength(20).IsRequired();}}
}
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
// MyDbContext.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;namespace TreeDemo
{class MyDbContext : DbContext{public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder){string connStr = "Server=.;Database=CoreDataDB;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true";optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(connStr);optionsBuilder.LogTo(Console.WriteLine);}protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder){base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);modelBuilder.ApplyConfigurationsFromAssembly(this.GetType().Assembly);}}
}
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
// 迁移数据库
PM> add-migration init
Build started...
Build succeeded.
The Entity Framework tools version '5.0.4' is older than that of the runtime '5.0.7'. Update the tools for the latest features and bug fixes.
To undo this action, use Remove-Migration.
PM> update-database
Build started...
Build succeeded.
The Entity Framework tools version '5.0.4' is older than that of the runtime '5.0.7'. Update the tools for the latest features and bug fixes.
Applying migration '20251006154758_init'.
Done.
PM>
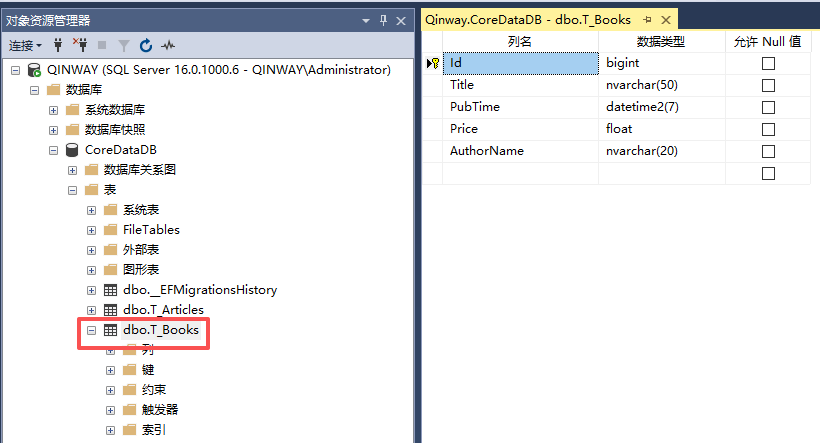
- 查看数据表
1.4 理解表达式树示例:Program.cs
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @1 构建表达式树Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @2 构建表达式树,将两个价格相加using ( MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){}}}
}说明:
1. 在@1处等号右边b => b.Price > 5是表达式树,等号左边Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1是表达式树类型。
2. 在@2处等号右边(b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price是表达式树,等号左边Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2是表达式树类型。
2. 断点调试
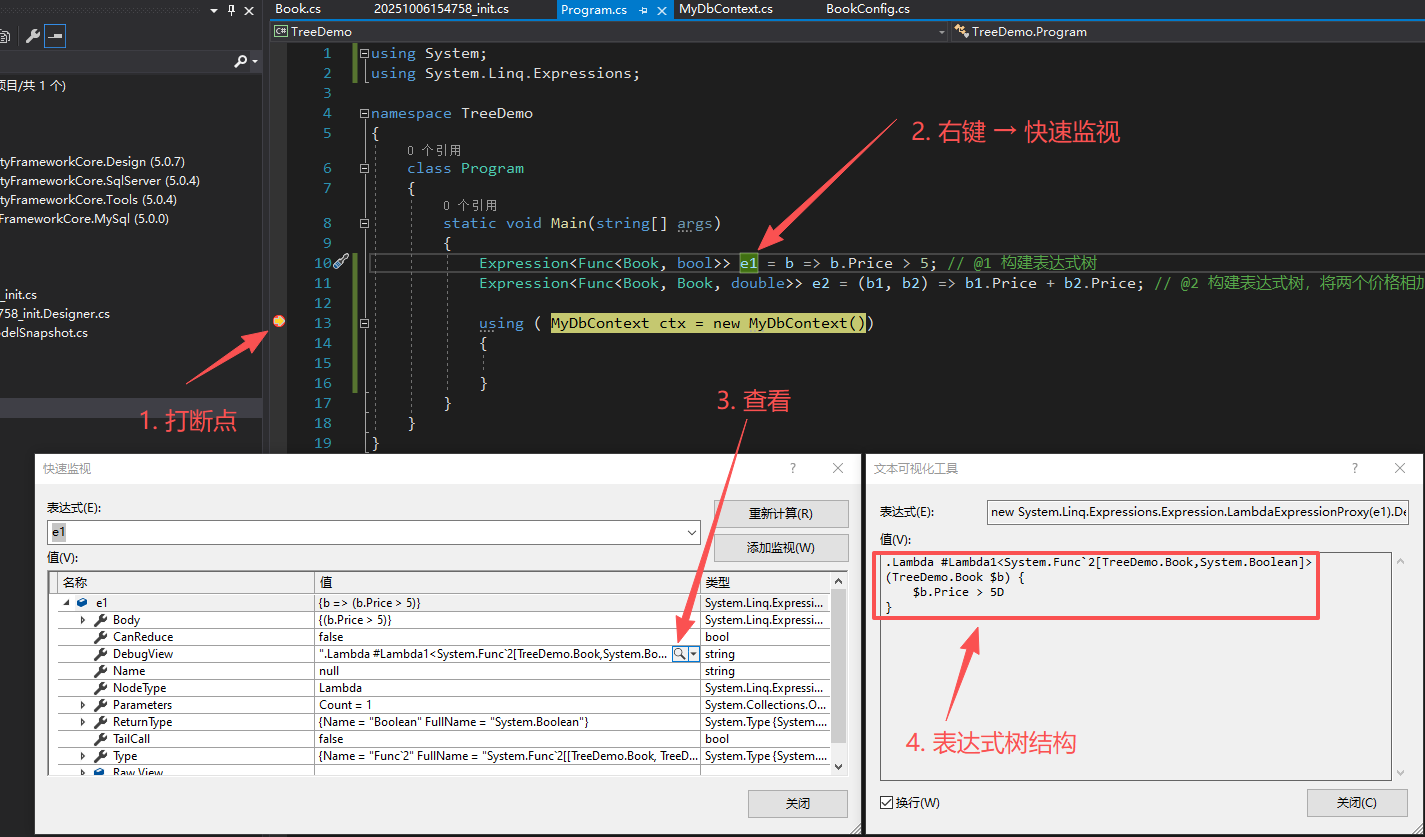
2.1 查看e1根节点:Body
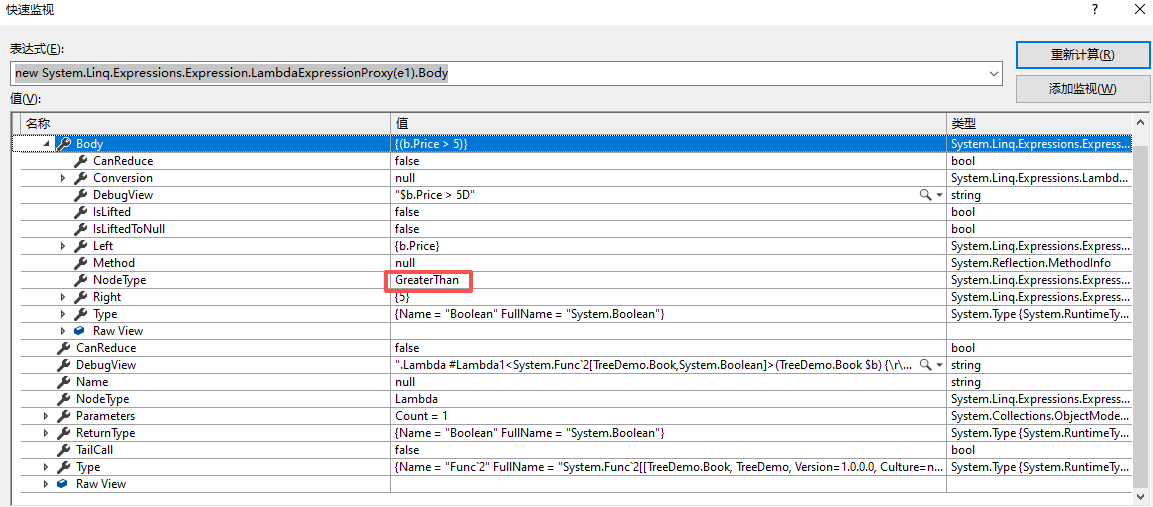
- 对照C#语句
Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5;
- NodeType → GreaterThan
- 节点类型:大于。表示根节点是一个大于号。
- Right →
- 右。大于号右边是5。
- Left →
- 左。大于号左边是b.Price
2.3 查看左节点:e1 → Body → Left
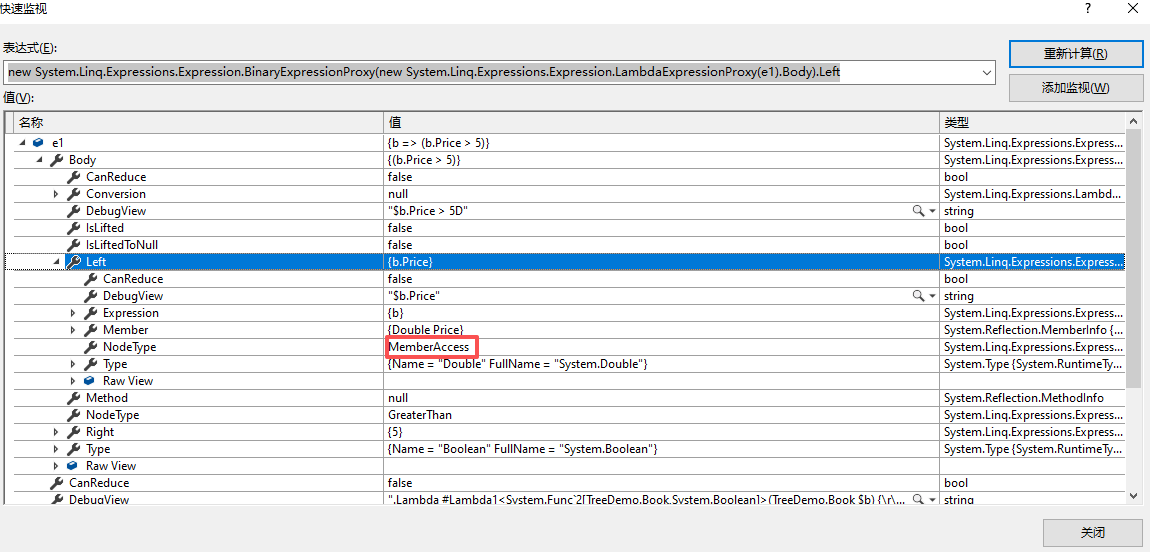
- NodeType → MemberAccess
- 节点访问。
- Expression →
- 表达式
- Member →
- 成员
2.4 查看e2根节点
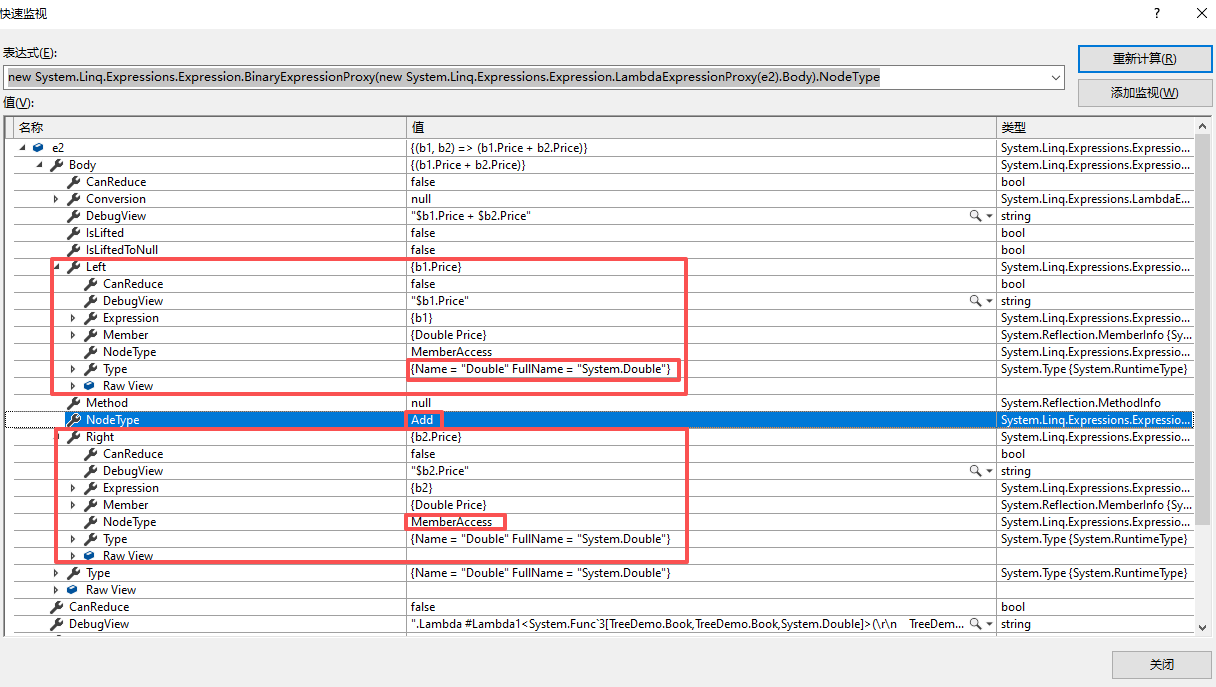
2.5 结论
- 在运行时,通过调试可以看到表达式树结构。
3. Expression和委托的关系和区别
3.1 去掉Expression编译也能通过
1、把Expression<Func<Book, bool>>换成Func<Book, bool>,写成下面的版本:
Func<Book, bool> e = b => b.Price > 5;
ctx.Books.Where(e).ToList();
查看生成的SQL。
2、Expression对象储存了运算逻辑,它把运算逻辑保存成抽象语法树(AST),可以在运行时动态获取运算逻辑。而普通委托则没有。
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
// Program.cs
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @1 构建表达式树Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @2 构建表达式树,将两个价格相加Func<Book, bool> f1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @3 构建表达式树Func<Book, Book, double> f2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @4 构建表达式树using ( MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){}}}
}
3.2 查看f1、f2节点
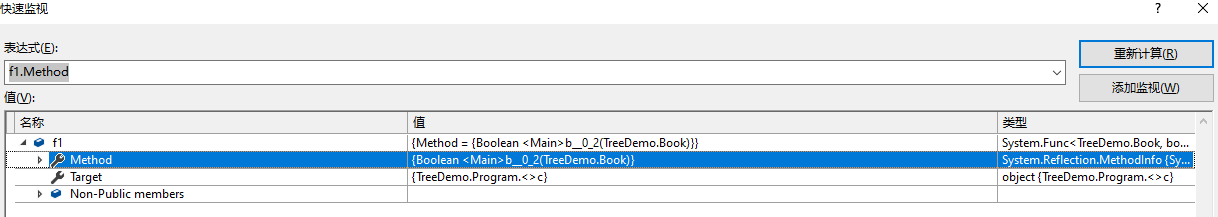
- 此时没有左、右等信息
- 使用Expression,编译器会帮我们构建表达式树。
- 使用Func,就是一个普通的委托,在运行时看不到表达式树结构
4. 查看SQL语句
4.1 查看e1的SQL语句
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @1 构建表达式树Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @2 构建表达式树,将两个价格相加Func<Book, bool> f1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @3 构建表达式树Func<Book, Book, double> f2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @4 构建表达式树using ( MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){ctx.Books.Where(e1).ToArray(); // Where参数为Book的返回值,以及bool类型。可以使用表达式树}}}
}// 查看SQL
SELECT [t].[Id], [t].[AuthorName], [t].[Price], [t].[PubTime], [t].[Title]FROM [T_Books] AS [t]WHERE [t].[Price] > 5.0E0说明:EF Core能够识别出来e1这个表达式树里面的东西,然后把表达式树种的内容翻译为SQL语句。
4.2 查看f1的SQL语句
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @1 构建表达式树Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @2 构建表达式树,将两个价格相加Func<Book, bool> f1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @3 构建表达式树?no,是一个委托。Func<Book, Book, double> f2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @4 构建表达式树? no,是一个委托。using ( MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){ctx.Books.Where(f1).ToArray(); // 一次取出所有数据,存放在内存中。}}}
}// 查看SQL
SELECT [t].[Id], [t].[AuthorName], [t].[Price], [t].[PubTime], [t].[Title]FROM [T_Books] AS [t]说明:
1. EF Core能够识别f1的东西,一下子把T_Books表里面所有东西都查出来,但是没有 WHERE [t].[Price] > 5.0E0的相关语句。
2. EF Core是把所有数据都取出来了,无法识别表达式树结构。而是在运行时,将数据存放在内存中,需要我们在内存中去找相关内容。
3. 注意f1是一个委托,而e1是一个表达式树。
4.3 给数据库添加一条数据
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static async Task Main(string[] args){using (MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){Book b1 = new Book { AuthorName = "杨中科", Title = "零基础趣学C语言", Price = 59.8, PubTime = new DateTime(2019, 3, 1) };Book b2 = new Book { AuthorName = "Robert Sedgewick", Title = "算法第4版", Price = 99, PubTime = new DateTime(2012, 10, 1) };Book b3 = new Book { AuthorName = "吴军", Title = "数学之美", Price = 69, PubTime = new DateTime(2020, 5, 1) };Book b4 = new Book { AuthorName = "杨中科", Title = "程序员的SQL经典", Price = 52, PubTime = new DateTime(2008, 9, 1) };Book b5 = new Book { AuthorName = "吴军", Title = "文明之光", Price = 246, PubTime = new DateTime(2017, 3, 1) };ctx.Books.Add(b1);ctx.Books.Add(b2);ctx.Books.Add(b3);ctx.Books.Add(b4);ctx.Books.Add(b5);await ctx.SaveChangesAsync();}Console.WriteLine("数据插入成功");Console.ReadLine();}}
}控制台输出:
数据插入成功
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
// 查看数据
Id Title PubTime Price AuthorName
3 零基础趣学C语言 2019-03-01 00:00:00.0000000 59.8 杨中科
4 算法第4版 2012-10-01 00:00:00.0000000 99 Robert Sedgewick
5 数学之美 2020-05-01 00:00:00.0000000 69 吴军
6 程序员的SQL经典 2008-09-01 00:00:00.0000000 52 杨中科
7 文明之光 2017-03-01 00:00:00.0000000 246 吴军
4.4 通过f1获取数据(获取所有)
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price;// Func<Book, bool> f1 = b => b.Price > 5; Func<Book, bool> f1 = b => { Console.WriteLine("查到了:"); return b.Price > 200; };Func<Book, Book, double> f2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; using (MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){ctx.Books.Where(f1).ToArray();}}}
}控制台输出:
查到了:
查到了:
查到了:
查到了:
查到了:// 查看SQL
SELECT [t].[Id], [t].[AuthorName], [t].[Price], [t].[PubTime], [t].[Title]FROM [T_Books] AS [t]说明:
1. 价格大于200的实际上只有Id = 7的一条数据,但是输出了5个查到了。
2. EF Core生成的SQL语句中并没有做Where b.Preice > 5检查。
3. 说明确实将所有数据都取出来了,那么有5条就输出5个查到了。
5. 查看表达式树结构(视频3-42)
5.1 VS内置查看AST
1、Visual Studio中调试程序,然后用【快速监视】的方式查看变量e的值,展开Raw View。
2、整个表达式树是一个“或”(OrElse)类型的节点,左节点(Left)是b.Price>5表达式,右节点(Right)是b.AuthorName.Contains("杨中科")表达式。而b.Price>5这个表达式又是一个“大于”(GreaterThan)类型的节点,左节点(Left)是b.Price,右节点(Right)是5。
3、AST:抽象语法树。
5.2 ExpressionTreeVisualizer可视化
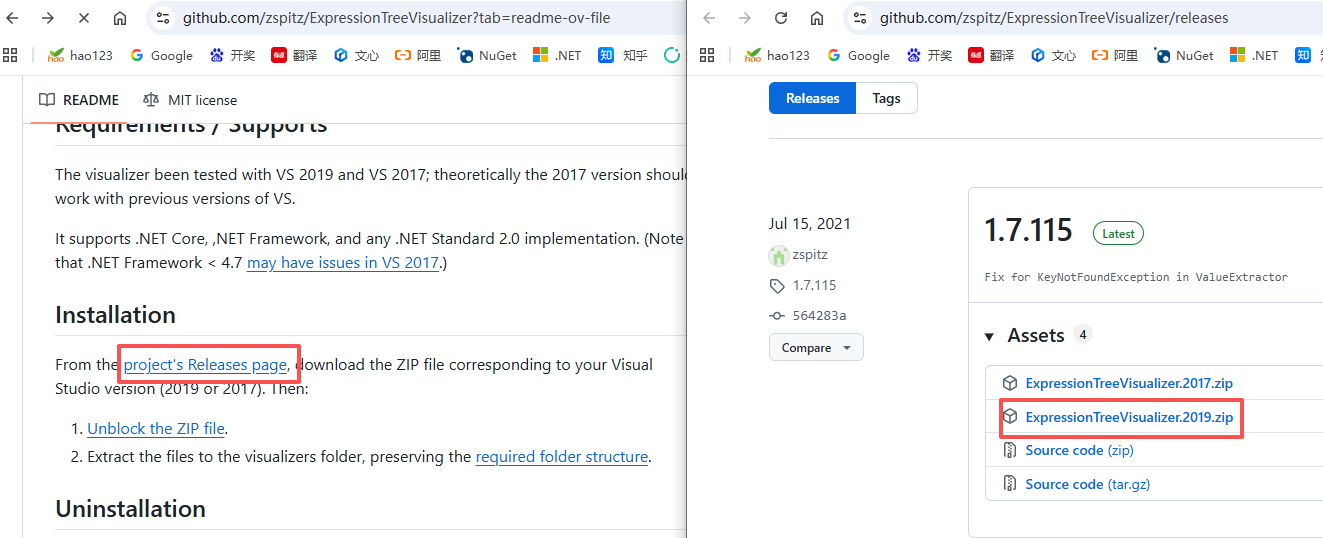
1、zspitz开发的ExpressionTreeVisualizer https://github.com/zspitz/ExpressionTreeVisualizer
安装VS插件。
2、目前:如果项目的.NET Core版本是5,那么可视化查看就会报BadImageFormatException异常,只能把项目降级到.NET Core 3.1才可以。
- 项目框架降低到.NET Core 3.1
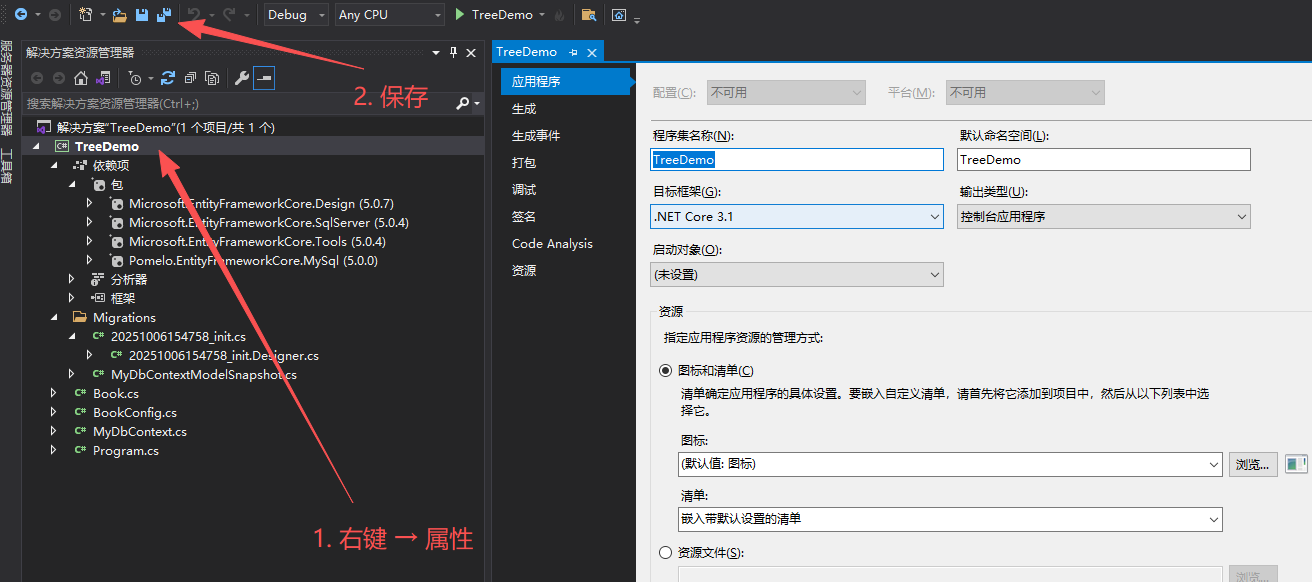
5.3 VS配置ExpressionTreeVisualizer
- Visual Studio版本:2019
- ExpressionTreeVisualizer版本:ExpressionTreeVisualizer.2019
- 下载方式:如下图
- 安装过程
step1 → 解压ExpressionTreeVisualizer.2019
step2 → 可能有防火墙报警,站点上有解决方法。
step3 → 站点上有具体用法,老师嫌麻烦就跳过了。-_-
- 不做演示,效果如下图。
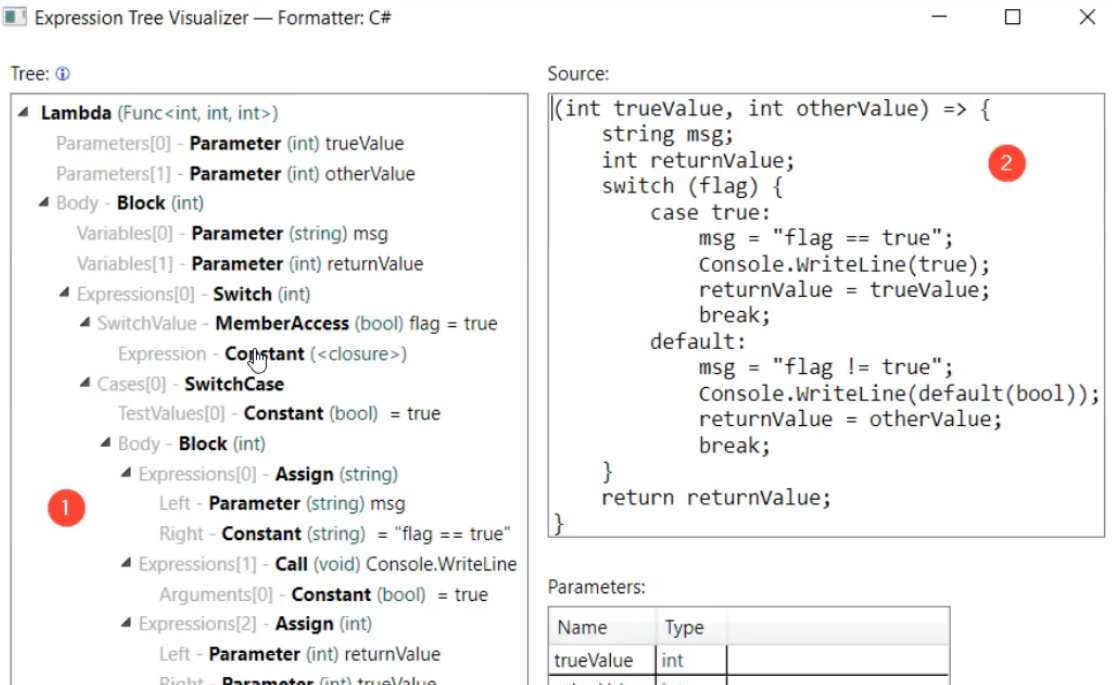
6. 通过代码查看AST
1、Install-Package ExpressionTreeToString
2、Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e = b => b.AuthorName.Contains("杨中科")||b.Price>30;
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString("Object notation", "C#"));
6.1 安装包
PM> Install-Package ExpressionTreeToString -VERSION 3.4.65
6.2 查看e1表达式树
using ExpressionTreeToString;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; // @1Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price; // @2Console.WriteLine(e1.ToString("Object notation", "C#")); // 这里ToString是ExpressionTreeToString里面的扩展方法,而不是编译器的using (MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){}}}
}控制台输出:
var b = new ParameterExpression { // 表达式树,与@1对应Type = typeof(Book),IsByRef = false,Name = "b"
};new Expression<Func<Book, bool>> {NodeType = ExpressionType.Lambda,Type = typeof(Func<Book, bool>),Parameters = new ReadOnlyCollection<ParameterExpression> {b},Body = new BinaryExpression {NodeType = ExpressionType.GreaterThan,Type = typeof(bool),Left = new MemberExpression {Type = typeof(double),Expression = b,Member = typeof(Book).GetProperty("Price")},Right = new ConstantExpression {Type = typeof(double),Value = 5}},ReturnType = typeof(bool)
}
6.3 查看e2表达式树
using ExpressionTreeToString;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace TreeDemo
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e1 = b => b.Price > 5; Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> e2 = (b1, b2) => b1.Price + b2.Price;Console.WriteLine(e2.ToString("Object notation", "C#")); // 查看e2using (MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){}}}
}控制台输出:
var b1 = new ParameterExpression {Type = typeof(Book),IsByRef = false,Name = "b1"
};
var b2 = new ParameterExpression {Type = typeof(Book),IsByRef = false,Name = "b2"
};new Expression<Func<Book, Book, double>> {NodeType = ExpressionType.Lambda,Type = typeof(Func<Book, Book, double>),Parameters = new ReadOnlyCollection<ParameterExpression> {b1,b2},Body = new BinaryExpression {NodeType = ExpressionType.Add,Type = typeof(double),Left = new MemberExpression {Type = typeof(double),Expression = b1,Member = typeof(Book).GetProperty("Price")},Right = new MemberExpression {Type = typeof(double),Expression = b2,Member = typeof(Book).GetProperty("Price")}},ReturnType = typeof(double)
}
7. 通过代码动态构造表达式树(视频3-43)
7.1 动态创建表达式树原理
1、只有通过代码动态构建表达式树才能更好的发挥表达式树的能力。
2、ParameterExpression(参数表达式)、BinaryExpression(二元运算表达式)、MethodCallExpression(方法调用表达式)、ConstantExpression(常量表达式)、MemberExpression(属性表达式)、LambdaExpression(Lambda表达式)等类几乎都没有提供构造方法,而且所有属性也几乎都是只读的,因此我们一般不会直接创建这些类的实例,而是调用Expression类的Parameter、MakeBinary、Call、Constant等静态方法来生成,这些静态方法我们一般称作创建表达式树的工厂方法,而属性则通过方法参数类设置。
7.2 动态创建表达式树示例
目标:生成和如下硬编码的C#代码一样的表达式树 → Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e = b =>b.Price > 5
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
ParameterExpression paramB = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Book),"b");
MemberExpression exprLeft = Expression.MakeMemberAccess(paramB, typeof(Book).GetProperty("Price"));
ConstantExpression exprRight = Expression.Constant(5.0,typeof(double));
BinaryExpression exprBody = Expression.MakeBinary(ExpressionType.GreaterThan, exprLeft, exprRight);
Expression<Func<Book, bool>> expr1 = Expression.Lambda<Func<Book, bool>>(exprBody, paramB);
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
using ExpressionTreeToString;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace TreeDemo
{/* Expression<Func<Book, bool>> e = b =>b.Price > 5对应的目标表达式树如下* * var b = new ParameterExpression { // @1Type = typeof(Book),IsByRef = false,Name = "b"};new Expression<Func<Book, bool>> { // @5NodeType = ExpressionType.Lambda,Type = typeof(Func<Book, bool>),Parameters = new ReadOnlyCollection<ParameterExpression> {b},Body = new BinaryExpression { // @4NodeType = ExpressionType.GreaterThan,Type = typeof(bool),Left = new MemberExpression { // @3Type = typeof(double),Expression = b,Member = typeof(Book).GetProperty("Price")},Right = new ConstantExpression { // @2Type = typeof(double),Value = 5}},ReturnType = typeof(bool)}*/class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ParameterExpression paramExpB = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Book), "b"); // 创建参数节点。与@1对应。ConstantExpression constExp5 = Expression.Constant(5 * 1.0, typeof(double)); // 创建常量节点。与@2对应。注意这里的类型5默认为int,需要转换为double与Price对应。MemberExpression memExpPrice = Expression.MakeMemberAccess(paramExpB, typeof(Book).GetProperty("Price")); // 创建属性节点。与@3对应。BinaryExpression binExpGreaterThan = Expression.GreaterThan(memExpPrice, constExp5); // 创建二元运算节点,与@4对应。Expression<Func<Book, bool>> lamExpRoot = Expression.Lambda<Func<Book, bool>>(binExpGreaterThan, paramExpB); // 创建Lambda节点,与@5对应。using (MyDbContext ctx = new MyDbContext()){ctx.Books.Where(lamExpRoot).ToArray();}Console.WriteLine("手动创建成功!");}}
}控制台输出:
手动创建成功!// 查看SQL
SELECT [t].[Id], [t].[AuthorName], [t].[Price], [t].[PubTime], [t].[Title]FROM [T_Books] AS [t]WHERE [t].[Price] > 5.0E0
—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—·—
// 查看4.1小结中的SQL
SELECT [t].[Id], [t].[AuthorName], [t].[Price], [t].[PubTime], [t].[Title]FROM [T_Books] AS [t]WHERE [t].[Price] > 5.0E0说明:
1. 本例和4.1小结中的SQL一致。
2. 手动创建表达式树的思路:先创建叶子节点,然后拼接为数。
7.3 工厂方法
Add:加法;
AndAlso:短路与运算;
ArrayAccess:数组元素访问;
Call:方法访问;
Condition:三元条件运算符;
Constant:常量表达式;
Convert:类型转换;
GreaterThan:大于运算符;
GreaterThanOrEqual:大于或等于运算符;
MakeBinary:创建二元运算;
NotEqual:不等于运算;
OrElse:短路或运算;
Parameter:表达式的参数;
结尾
书籍:ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1pK41137He
著:杨中科
ISBN:978-7-115-58657-5
版次:第1版
发行:人民邮电出版社
※敬请购买正版书籍,侵删请联系85863947@qq.com※
※本文章为看书或查阅资料而总结的笔记,仅供参考,如有错误请留言指正,谢谢!※
