一、什么是布局
在 Qt Quick 中有两套与元素布局相关的类库,一套叫作 Item Positioner(定位器),一套叫作 Item Layout(布局)。其实在 Qt Quick 中还有一个 锚布局,它通过 Item 的 anchors 属性实现,是 Qt Quick 中非常灵活的一种布局方式。
我们可以在终端中使用 pip 安装 PySide6 模块。默认是从国外的主站上下载,因此,我们可能会遇到网络不好的情况导致下载失败。我们可以在 pip 指令后通过 -i 指定国内镜像源下载。
pip install pygame -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
国内常用的 pip 下载源列表:
- 阿里云 https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
- 中国科技大学 https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple
- 清华大学 https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
- 中国科学技术大学 http://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple
二、锚布局
在 QML 中,锚点(anchors)是一种用于定义元素之间相对位置和大小关系的机制。锚点允许你指定一个元素相对于其父元素或其他元素的位置和尺寸。通过使用锚点,你可以创建响应式布局,使 QML 界面能够根据不同屏幕尺寸和分辨率进行自适应调整。
QML 中的每个元素都有一个隐式的锚点系统,你可以通过 anchors 属性来访问它。anchors 属性提供了多个属性来设置锚点的位置。
每个 Item 都有 7 条不可见的锚线:上(top)、下(bottom)、左(left)、右(right)、水平中心(horizontalCenter)、垂直中心(verticalCenter)和 基线(baseline)。

anchors.top // 将元素的顶部边缘锚定到某个参考点的顶部边缘
anchors.bottom // 将元素的底部边缘锚定到某个参考点的底部边缘
anchors.left // 将元素的左边缘锚定到某个参考点的左边缘
anchors.right // 将元素的右边缘锚定到某个参考点的右边缘anchors.horizontalCenter // 将元素的水平中心锚定到某个参考点的水平中心
anchors.verticalCenter // 将元素的垂直中心锚定到某个参考点的垂直中心anchors.fill // 使元素填充其父元素或参考元素的整个区域
baseline是指文本所在的线,如果Item没有文字,则baseline就和top的位置相同。
我们还可以使用 margins 属性设置四个边的边距。

anchors.margins // 设置元素与其锚点之间的外边距
anchors.leftMargin // 设置元素与其锚点之间的左边距
anchors.rightMargin // 设置元素与其锚点之间的右边距
anchors.topMargin // 设置元素与其锚点之间的顶边距
anchors.bottomMargin // 设置元素与其锚点之间的底边距
我们新建一个 template.py 文件。
import sysfrom PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication
from PySide6.QtQml import QQmlApplicationEngineif __name__ == "__main__":app = QApplication(sys.argv) # 1.创建一个QApplication类的实例engine = QQmlApplicationEngine() # 2.创建QML引擎对象engine.load("template.qml") # 3.加载QML文件sys.exit(app.exec()) # 4.进入程序的主循环并通过exit()函数确保主循环安全结束
我们新建一个 template.qml 文件。
import QtQuick.Window// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个文本(Text)元素Text {id: titleTextId // 定义一个标识text: "Custom Layout Example" // 设置文本元素的内容font.pointSize: 24 // 设置文本的字体大小color: "#FFCCCC" // 设置字体颜色// 使用锚点(anchors)系统来定位文本元素anchors.top: parent.top // 将顶部的锚点定位到父元素的顶部anchors.topMargin: 20 // 设置顶部边距为20像素anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter // 水平居中}// 定义一个文本(Text)元素Text {text: "This is an exmaple of using anchors for layout." // 设置文本元素的内容font.pointSize: 18 // 设置文本的字体大小color: "#FF99CC" // 设置字体颜色// 使用锚点(anchors)系统来定位文本元素anchors.top: titleTextId.bottom // 将顶部的锚点定位到指定控件父的底部anchors.topMargin: 20 // 设置顶部边距为20像素anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter // 水平居中}// 定义一个Item元素Item {width: 300 // 宽度height: 300 // 高度// 使用锚点(anchors)系统来定位文本元素,这里中心的锚点定位到其父元素的中心anchors.centerIn: parentRectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色anchors.fill: parent // 填充父容器对象Text {text: "Hello Sakura!"font.pointSize: 18color: "#FFFFFF"anchors.top: parent.top // 将顶部的锚点定位到指定控件父的顶部anchors.topMargin: 10 // 设置顶部边距为10像素anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter // 水平居中}}}// 定义一个矩形元素Rectangle {width: 100 // 宽度height: 50 // 高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色// 使用锚点(anchors)系统来定位文本元素anchors.left: parent.left // 将左侧的锚点定位到父元素的左侧anchors.leftMargin: 20 // 设置左侧边距为20像素anchors.bottom: parent.bottom // 将底部的锚点定位到父元素的底部anchors.bottomMargin: 20 // 设置底部边距为20像素}// 定义一个矩形元素Rectangle {width: 100 // 宽度height: 50 // 高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色anchors.right: parent.right // 将右侧的锚点定位到父元素的右侧anchors.rightMargin: 20 // 设置右侧边距为20像素anchors.bottom: parent.bottom // 将底部的锚点定位到父元素的底部anchors.bottomMargin: 20 // 设置底部边距为20像素}
}
当你使用锚点时,请确保你指定的参考点(如父元素或其他元素)是有效的,并且它们在布局中是可见的。
锚点系统是基于父元素或参考元素的坐标系统来工作的,因此如果父元素或参考元素的大小或位置发生变化,依赖于它们的子元素也会相应地发生变化。
在使用锚点时,要注意避免循环依赖或相互冲突的锚点设置,这可能会导致布局问题或不可预测的行为。
三、定位器
定位器 是一种 容器元素,专门用来管理界面中的其它元素。如果定位器中的子项目不可见(visible 为 false)、宽度或者高度为0,那么该子项目不会显示,也不会被布局。定位器可以自动布局其子项目,也就是说,其子项目不再需要显式设置 x、y等属性或使用锚 anchors 进行布局。
定位器 不会改变它管理的元素的大小,即便用户调整了界面尺寸,它也坚持不干涉孩子们的尺寸,这可能与你的期望不同,不过如果你希望使用“自动根据界面尺寸变化调整孩子们的尺寸”这种特性,可以使用 Qt Quick 中的 布局管理器。
定位器 包括 Row(行定位器)、Column(列定位器)、Grid(栅格定位器)、Flow(流式定位器)。
3.1、行定位器
Row 沿着一行安置它的孩子们。一旦你把一个 Item 交给 Row 来管理,那就不要再使用 Item 的x、y、anchors 等属性了。在一个 Row 内的 Item,可以使用 Positioner 附加属性来获知自己在 Row 中的详细位置信息。Positioner 有 index、isFirstItem、isLastItem 三个属性。
Row 有一个 spacing 属性,用来指定它管理的 Item 之间的 间隔。还有一个 layoutDirection 属性,可以指定 布局方向,取值为 Qt.LeftToRight 时 从左到右 放置 Item,这是默认行为,取值为 Qt.RightToLeft 时 从右向左 放置 Item。
Row 还有 add、move、populate 三个 Transition 类型的属性,分别指定应用于 Item 添加、Item 移动、定位器初始化创建Items 三种场景的过渡动画。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个Row,用于水平布局Row {anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心spacing: 100 // 用于设置子元素之间的间隔layoutDirection: Qt.RightToLeft // 设置布局的显示方向为从右到左Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 50 // 高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}}
}
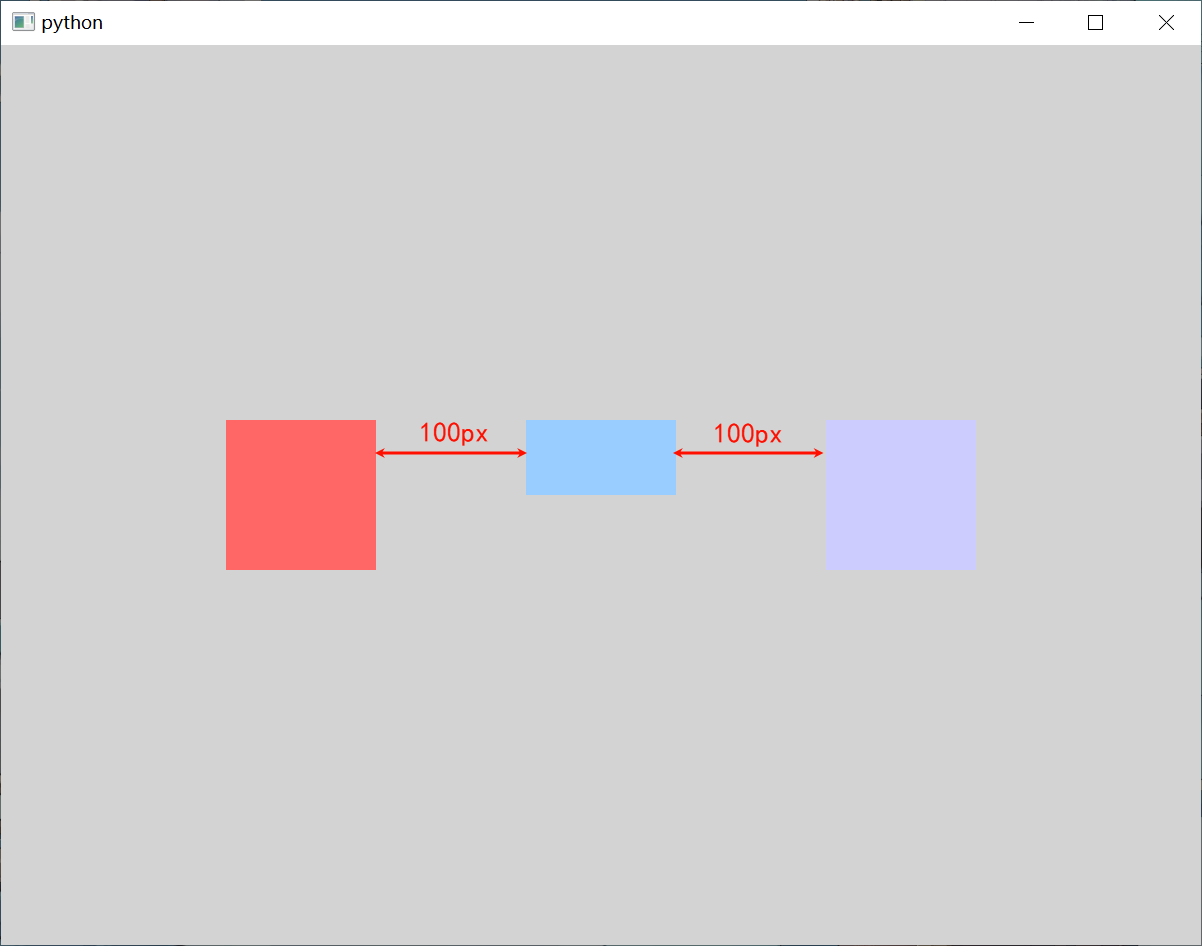
Row本身也是一个Item,可以使用anchors布局来决定它在父Item中的位置。如果
Row中的Item不是visible,或者其宽度或高度为 0,则该项目将不会布局,在行中也不可见。
3.2、列定位器
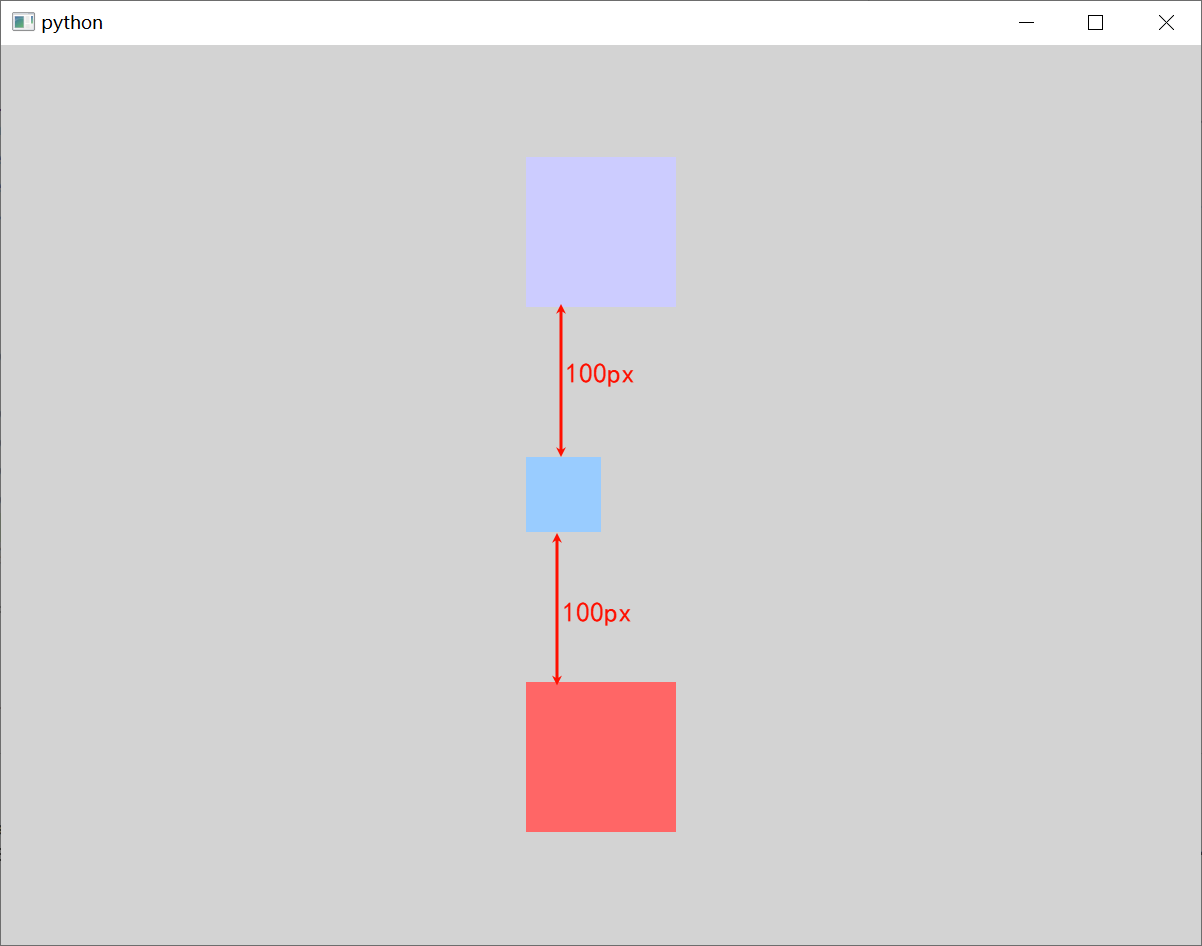
Column 与 Row 类似,不过是在垂直方向上安排它的子Item。Column 的 spacing 属性描述子 Item 之间的间隔。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个Column,用于垂直布局Column {anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心spacing: 100 // 用于设置子元素之间的间隔Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 50 // 宽度height: 50 // 高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}}
}
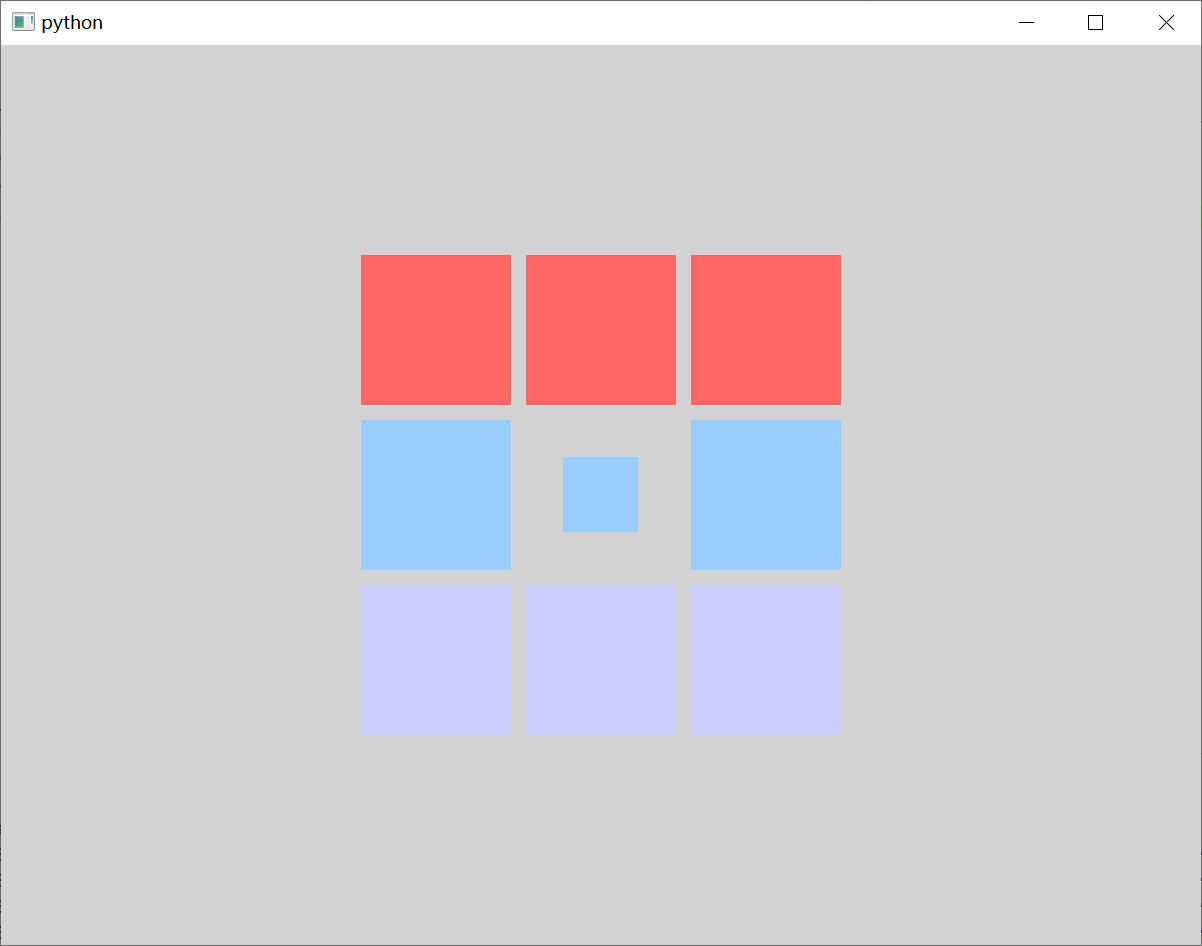
3.3、栅格定位器
Grid 在一个网格上安置它的子 Item,它会创建一个拥有很多单元格的网格,足够容纳它的所有子 Item。Grid 会从左到右、从上到下把它的子 Item 一个个塞到单元格里。Item 默认会被放在一个单元格左上角,即 (0, 0) 位置。
我们可以通过 Grid 的 rows 和 columns 属性 指定表格的行、列数。如果不设置,默认只有 4 列,而行数则会根据实际的 Item 数量自动计算。rowSpacing 和 columnSpacing 属性用来 指定行、列间距,单位是像素。
Grid 的 flow 属性 描述表格的流模式,Grid.LeftToRight 是默认值,这种流模式 从左到右 一个挨一个放置 Item,一行放满再放下一行。flow 取值为 Grid.TopToBottom 时,从上到下 一个挨一个放置 Item,一列放满再放下一列。
Grid 的 horizontalItemAlignment 和 verticalItemAlignment 属性用来 指定单元格对齐方式。默认的单元格对齐方式和 layoutDirection 以及 flow 有关。
horizontalItemAlignment的有效值是Grid.AlignLeft、Grid.AlignRight和Grid.AlignHCenter。verticalItemAlignment的有效值是Grid.AlignTop、Grid.AlignBottom和Grid.AlignVCenter。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个GridLayout,用于网格布局Grid {anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心rows: 3 // 设置行数columns: 3 // 设置列数rowSpacing: 10 // 设置行间距columnSpacing: 10 // 设置列间距horizontalItemAlignment: Grid.AlignHCenter // 设置水平对齐方式verticalItemAlignment: Grid.AlignVCenter // 设置垂直对齐方式Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 50 // 宽度height: 50 // 高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {width : 100 // 宽度height: 100 // 高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}}
}
3.4、流式定位器
在 QML 中,Flow 是一种非常灵活的布局方式,它允许元素根据容器的尺寸和元素的尺寸自动进行排列,类似于文本排版中的 “流” 概念,元素会按照指定的方向(通常是水平或垂直)依次排列,当一行或一列无法容纳更多元素时,会自动换行或换列。
Flow 的 flow 属性,默认取值 Flow.LeftToRight,从左到右 安排 Item,直到 Flow 本身的宽度不能容纳新的子 Item 时折行。当 flow 取值 Flow.TopToBottom 时,从上到下 安排 Item,直到 Flow 本身的高度不能容纳新的子 Item 时开始在下一列上安排 Item。在 QML 中,我们还可以通过 spacing 属性来 设置元素之间的间距。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个Flow,用于流式布局Flow {width: parent.width // 宽度height: parent.height // 高度 anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的spacing: 100 // 用于设置子元素之间的间隔// Repeater是一个用于根据模型(通常是列表或数组)动态生成一组子元素的有用工具Repeater{// 定义了数据源,通常是一个列表或数组。model: 18 // 设置重读的次数// 定义了如何显示模型中的每个项目,它是一个包含要实例化的 QML 元素的组件。delegate: Rectangle{width: 100height: 100color: Qt.rgba(Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1)}}}
}

四、布局管理器
Qt Quick 中的 布局管理器 是一组用于在用户界面中排列项目的类型。布局管理器 不仅进行布局,而且会改变子 Item 的大小,所以更适用于需要改变用户界面大小的应用。因为布局管理器也是继承自 Item,所以它们可以嵌套。布局管理器 包括 行布局(RowLayout)、列布局(ColumnLayout)、表格布局(GridLayout)。
4.1、水平布局管理器
在 QML 中,水平布局通常是通过 RowLayout 来实现的。RowLayout 是一种布局管理器,它允许你将子元素水平地排列在一行中。RowLayout 有一个 spacing 属性,用来 指定它管理的 Item 之间的间隔。还有一个 layoutDirection 属性,可以 指定布局方向,取值为 Qt.LeftToRight 时 从左到右放置 Item,这是默认行为,取值为 Qt.RightToLeft 时 从右向左放置 Item。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window
import QtQuick.Layouts// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个RowLayout,用于水平布局RowLayout {anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心spacing: 100 // 用于设置子元素之间的间隔layoutDirection: Qt.RightToLeft // 设置布局的显示方向为从右到左Rectangle {implicitWidth : 100 // 设置矩形的隐式宽度implicitHeight: 100 // 设置矩形的隐式高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {Layout.preferredWidth : 150 // 设置矩形的首选宽度Layout.preferredHeight : 50 // 设置矩形的首选高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {implicitWidth : 100 // 设置矩形的隐式宽度Layout.preferredHeight: 100 // 设置矩形的首选高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}}
}

在布局中如何要设置 Item 的宽度和高度,推荐使用
implicitWidth属性 和implicitHeight属性设置,或者使用Layout.preferredWidth和Layout.preferredHeight设置。
4.2、垂直布局管理器
在 QML 中,垂直布局通常是通过 ColumnLayout 来实现的。这些布局管理器允许你将子元素垂直地排列在一起。ColumnLayout 本身也是一个 Item,可以使用 anchors 布局来决定它在父 Item 中的位置。ColumnLayout 的 spacing 属性描述 子 Item 之间的间隔。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window
import QtQuick.Layouts// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个ColumnLayout,用于垂直布局ColumnLayout {height: parent.height // 高度anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心Rectangle {implicitWidth : 100 // 设置矩形的隐式宽度implicitHeight: 100 // 设置矩形的隐式高度color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {Layout.preferredWidth : 50 // 设置矩形的首选宽度Layout.preferredHeight : 50 // 设置矩形的首选高度color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}Rectangle {implicitWidth : 100 // 设置矩形的隐式宽度Layout.preferredHeight: 100 // 设置矩形的首选高度color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色}}
}
4.3、栅格布局管理器
在 QML 中,栅格布局是通过 GridLayout 来实现的。GridLayout 允许你将子元素放置在一个二维的网格中,并且可以指定网格的行数和列数,并控制每个元素在网格中的位置、大小和跨越多个单元格的能力。
你可以通过 GridLayout 的 rows 和 columns 属性 设定表格的行、列数,rowSpacing 和 columnSpacing 属性 指定行、列间距,单位是像素。
在每个 Item 项中,我们可以通过 Layout.row 和 Layout.column 属性 指定该项在栅格布局中的位置。我们还可以通过 Layout.rowSpan 和 Layout.columnSpan 属性 指定合并的行和列。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window
import QtQuick.Layouts// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个GridLayout,用于网格布局GridLayout {width: parent.width // 宽度height: parent.height // 高度 anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心rows: 3 // 设置行数columns: 3 // 设置列数rowSpacing: 10 // 设置行间距columnSpacing: 10 // 设置列间距Rectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色implicitWidth: 200 // 设置矩形的隐式宽度implicitHeight: 200 // 设置矩形的隐式高度Layout.row: 0 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 0 // 设置矩形所在的列}Rectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.preferredWidth: 200 // 设置矩形的首选宽度Layout.preferredHeight: 200 // 设置矩形的首选高度Layout.row: 0 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 1 // 设置矩形所在的列}Rectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色implicitWidth: 200 // 设置矩形的隐式宽度Layout.preferredHeight: 200 // 设置矩形的首选高度Layout.row: 0 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 2 // 设置矩形所在的列}Rectangle {color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.row: 1 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 0 // 设置矩形所在的列Layout.rowSpan: 2 // 占用二行Layout.columnSpan: 1 // 占用一列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.row: 1 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 1 // 设置矩形所在的列Layout.rowSpan: 1 // 占用一行Layout.columnSpan: 2 // 占用两列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.row: 2 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 1 // 设置矩形所在的列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.row: 2 // 设置矩形所在的行Layout.column: 2 // 设置矩形所在的列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}}
}
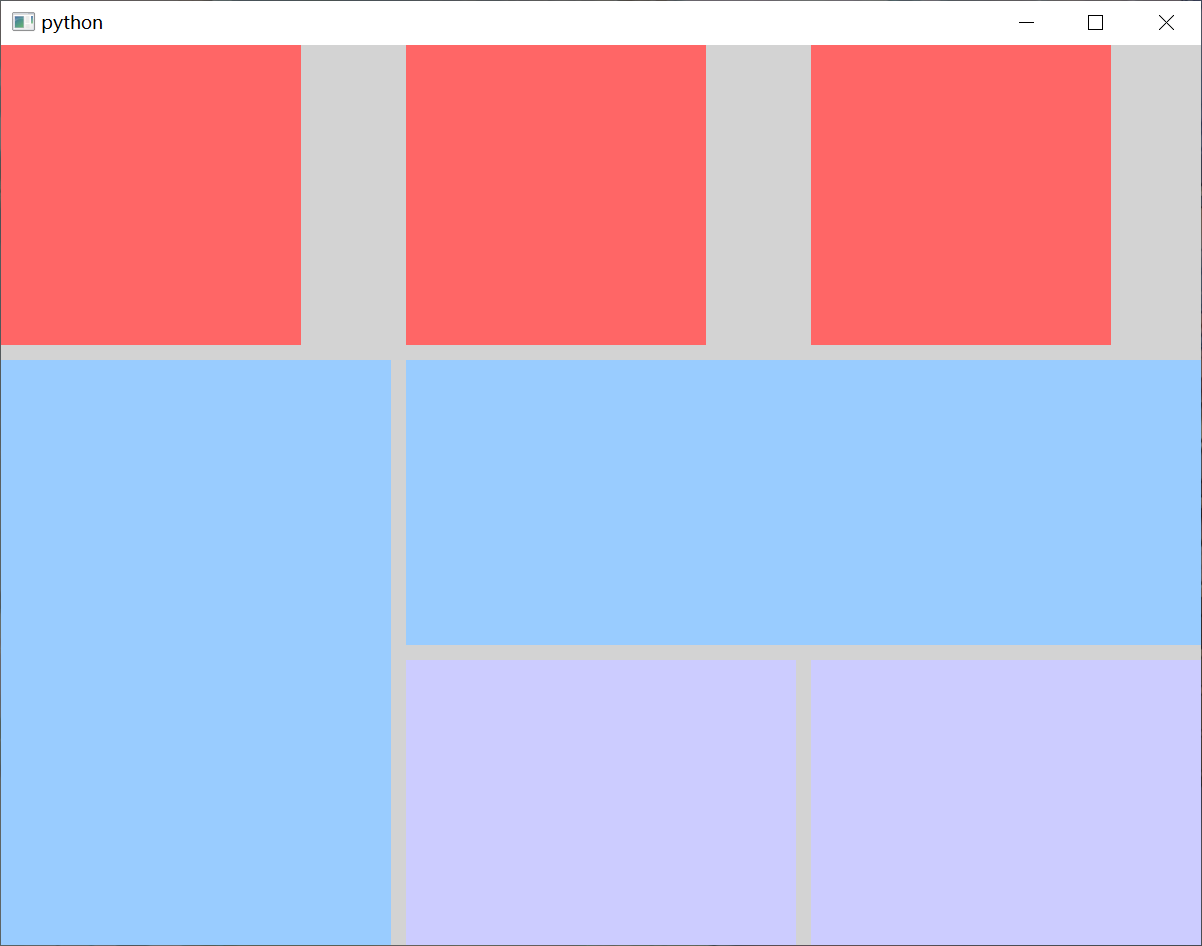
在栅格布局中,如果我们添加的子元素不指定行列信息,子元素会呈现水平布局或垂直布局。GridLayout 的 flow 属性描述 栅格布局的流模式,Grid.LeftToRight 是默认值,这种流模式从左到右一个挨一个放置 Item,一行放满再放下一行。flow 取值为Grid.TopToBottom 时,从上到下一个挨一个放置 Item,一列放满再放下一列。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window
import QtQuick.Layouts// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个GridLayout,用于网格布局GridLayout {width: parent.width // 宽度height: parent.height // 高度 anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心rows: 3 // 设置行数columns: 3 // 设置列数rowSpacing: 10 // 设置行间距columnSpacing: 10 // 设置列间距flow: Grid.TopToBottom // 设置布局方式Rectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.rowSpan: 2 // 占用二行Layout.columnSpan: 1 // 占用一列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.rowSpan: 1 // 占用一行Layout.columnSpan: 2 // 占用二列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#99CCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.rowSpan: 2 // 占用二行Layout.columnSpan: 1 // 占用一列Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}Rectangle {color: "#CCCCFF" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 设置矩形填充Column布局的高度}}
}

4.4、栈布局管理器
栈布局管理器 StackLayout 可以管理多个项目,但只能显示一个项目。可以通过 currentIndex 属性来 设置当前显示的项目,索引号对应布局管理器中子项目的顺序,从 0 开始。另外,StackLayout 还包含 index 和 isCurrentItem 等附加属性。
修改 template.qml 文件的内容。
import QtQuick.Window
import QtQuick.Layouts// Window控件表示一个顶级窗口
// 在QML中,元素是通过大括号{}内的属性来配置的。
Window {width: 800 // 窗口的宽度height: 600 // 窗口的高度visible: true // 显示窗口color: "lightgray" // 窗口的背景颜色// 定义一个StackLayout,用于栈布局StackLayout {id: stackLayoutId // IDwidth: parent.width // 宽度height: parent.height // 高度 anchors.centerIn: parent // 将中心的锚点定位到父元素的中心Rectangle {color: "#FF6666" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 填充宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 填充高度}Rectangle {color: "#66ffb0ff" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 填充宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 填充高度}Rectangle {color: "#6673ffff" // 设置矩形颜色Layout.fillWidth: true // 填充宽度Layout.fillHeight: true // 填充高度}}// 鼠标事件MouseArea {anchors.fill: parent // 填充父元素// 点击事件onClicked: {stackLayoutId.currentIndex = (stackLayoutId.currentIndex + 1) % stackLayoutId.count}}
}
