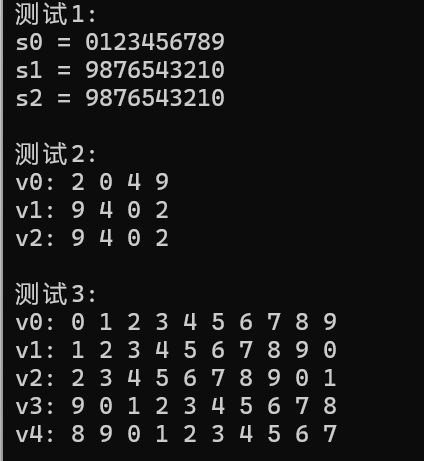
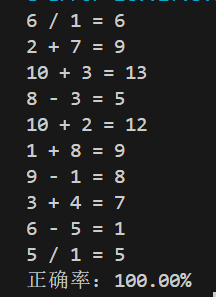#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); void test1(); void test2(); void test3(); int main() {std::cout << "测试1: \n";test1();std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";test2();std::cout << "\n测试3: \n";test3(); } template <typename T> void output(const T &c) {for(auto &i : c)std::cout << i << ' ';std::cout << '\n'; } void test1() {using namespace std;string s0{"0123456789"};cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl;string s1(s0);reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;string s2(s0.size(), ' ');reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin());cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; } void test2() {using namespace std;vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9};cout << "v0: "; output(v0);vector<int> v1{v0};reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());cout << "v1: "; output(v1);vector<int> v2{v0};reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin());cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } void test3() {using namespace std;vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};cout << "v0: "; output(v0);vector<int> v1{v0};rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end());cout << "v1: "; output(v1);vector<int> v2{v0};rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end());cout << "v2: "; output(v2);vector<int> v3{v0};rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end());cout << "v3: "; output(v3);vector<int> v4{v0};rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end());cout << "v4: "; output(v4); }
#回答问题
reverse将序列中的元素原地反转。reverse_copy将序列中的元素复制到另一个位置,并在复制过程中进行反转.
rotate(旋转)算法执行的操作可以最直观地理解为 一次循环左移。它将序列中的元素进行重新排列,使得序列的某一部分“旋转”到前面,而另一部分“旋转”到后面。
它的核心行为是:将 [first, last) 范围内的元素进行循环移位,使得 middle 所指向的元素成为新的第一个元素,而原来在 middle 之前的元素被移动到序列的末尾。
第一个参数first:旋转范围内的起始位置
第二个参数middle:旋转后成为新的第一个元素的位置,向左移动begin()+n,向右移动end()-n
第三个参数last:旋转范围内的结束位置.
#实验任务二
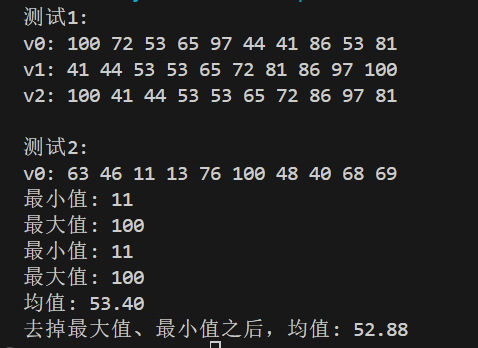
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime>template<typename T> void output(const T &c); int generate_random_number(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::srand(std::time(0)); std::cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); }template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) std::cout << i << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; }int generate_random_number() { return std::rand() % 101; }void test1() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); }void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); auto min_iter = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); auto max_iter = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *min_iter << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *max_iter << endl; auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0.0) / v0.size(); cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; sort(v0.begin(), v0.end()); double avg2 = accumulate(v0.begin()+1, v0.end()-1, 0.0) / (v0.size()-2); cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; }
#问题
1.generate的作用我认为是用指定的生成器函数为容器指定范围内的每个元素赋值;
2.minmax_element效率更高,只遍历一次容器,并且代码就一行更简洁;
3.效果等同 lambda表达式在这里是一个匿名函数对象,它的行为与generate_random_number完全一致,lambda不需要另外再声明定义,适用于短小的一次性逻辑。
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <cctype>unsigned char func(unsigned char c);void test1(); void test2();int main() {std::cout << "test1: string caps switch\n";test1();std::cout << '\n';std::cout << "test2: char switch\n";test2(); }unsigned char func(unsigned char c) {if (c == 'z')return 'a';if (c == 'Z')return 'A';if (isalpha(c))return static_cast<unsigned char>(c + 1);return c; }void test1() {using namespace std;string s1{ "Hello World 2077!" };cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;string s2;for (auto& c : s1)s2 += tolower(c);cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;string s3;for (auto& c : s1)s3 += toupper(c);cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl; }void test2() {using namespace std;string s1{ "Long Live The Republic!" };cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;string s2(s1.size(),' ');transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin(), func);cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; }
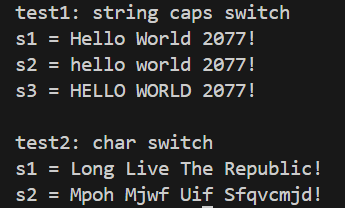
##回答问题
- func函数将字符进行加密,加密方法为所有字符(除了z)后移一个字符的凯撒变换;z变成a,这是特殊情况。
- tolower的功能是将字母字符变为小写字母,toupper的功能是将字母字符变为大写字母。
- 第一个:从哪里开始;第二个:到哪里结束;第三个:开始执行的位置;第四个:传递时附加的规则;改变后,会在原始容器内部执行操。
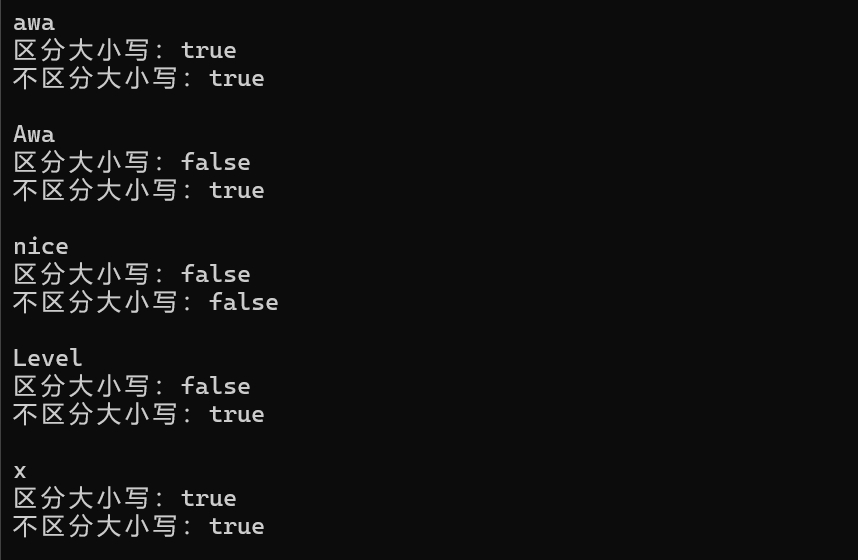
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <cctype>bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s); bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s);int main() {using namespace std;string s;while(cin >> s) {cout << boolalpha<< "区分大小写:" << is_palindrome(s) << "\n"<< "不区分大小写:" << is_palindrome_ignore_case(s) << "\n\n";} }// 以下两个函数需要补全 bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s) {using namespace std;string t=s;reverse(t.begin(),t.end()) ;if(t.compare(s)==0){return true;}else{return false;} }bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s) {using namespace std;string t=s,sl;for(auto i : s){sl+=tolower(i);}reverse(t.begin(),t.end()) ;string tl;for(auto i : t){tl+=tolower(i);}if(tl.compare(sl)==0){return true;}else{return false;} }
![image]()
##回答问题
-
使用
getline(cin, s)#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; string dec2n(int x, int n = 2);int main() {int x;while(cin >> x) {cout << "十进制: " << x << '\n'<< "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << '\n'<< "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n'<< "十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n'<< "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n'<< "三十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n";} }// 函数dec2n定义 string dec2n(int x, int n) {if (x == 0) {return "0";}string result;while (x > 0) {int t = x % n;result += (t>=10) ? ('A' + (t - 10)) : ('0' + t);x /= n;}reverse(result.begin(), result.end());return result; }
![8e622c897a22d032eadf97fd19b20b43]()
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> // 包含 std::rotate #include <iomanip> // 用于 setw 格式化输出using namespace std;int main() {string original = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";for (char c : original) {cout << c << " ";}cout << endl;for (int n = 1; n <= 26; ++n) {string cipher = original;rotate(cipher.begin(), cipher.begin() + n, cipher.end());cout << setw(2) << n << " ";for (char c : cipher) {cout << (char)toupper(c) << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0; }
![f7748de09275c619ed859c544ada8455_720]()
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime>int generate_number(); char generate_operator(std::string &s); int given();int main(){ using namespace std; srand(time(0)); int count = 0, result, r; for(auto i = 1; i < 11; i++) { result = given(); cin >> r; if(r == result) count++; } cout << "正确率:" << fixed << setprecision(2) << static_cast<double>(count*10) << "%"; }int generate_number(){ return std::rand() % 10 + 1; }char generate_operator(std::string &s){ return s[std::rand() % 4]; }int given(){ using namespace std; char c; int a, b; std::string op{"*/+-"}; c = generate_operator(op); a = generate_number(), b = generate_number(); if(c == '/') {while(a%b != 0) a = generate_number(), b = generate_number(); cout << a << " " << c << " " << b << " = "; return a/b; } else if(c == '-'){ while(a < b) a = generate_number(), b = generate_number(); cout << a << " " << c << " " << b << " = "; return a-b; } else if(c == '+'){ cout << a << " " << c << " " << b << " = "; return a+b; } else{ cout << a << " " << c << " " << b << " = "; return a*b; } }
![33769873efa5c431ebb103115a35546b]()