实验任务一:

1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 5 // 类T: 声明 6 class T { 7 // 对象属性、方法 8 public: 9 T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数 10 T(const T &t); // 复制构造函数 11 T(T &&t); // 移动构造函数 12 ~T(); // 析构函数 13 14 void adjust(int ratio); // 按系数成倍调整数据 15 void display() const; // 以(m1, m2)形式显示T类对象信息 16 17 private: 18 int m1, m2; 19 20 // 类属性、方法 21 public: 22 static int get_cnt(); // 显示当前T类对象总数 23 24 public: 25 static const std::string doc; // 类T的描述信息 26 static const int max_cnt; // 类T对象上限 27 28 private: 29 static int cnt; // 当前T类对象数目 30 31 // 类T友元函数声明 32 friend void func(); 33 }; 34 35 // 普通函数声明 36 void func(); 37 38 //const std::string T::doc{ "a simple class sample" }; 39 //const int T::max_cnt = 999; 40 //int T::cnt = 0;

1 #include "T.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 5 // 类T实现 6 7 // static成员数据类外初始化 8 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; 9 const int T::max_cnt = 999; 10 int T::cnt = 0; 11 12 // 类方法 13 14 15 // 对象方法 16 T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} { 17 ++cnt; 18 std::cout << "T constructor called.\n"; 19 } 20 21 T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 22 ++cnt; 23 std::cout << "T copy constructor called.\n"; 24 } 25 26 T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 27 ++cnt; 28 std::cout << "T move constructor called.\n"; 29 } 30 31 T::~T() { 32 --cnt; 33 std::cout << "T destructor called.\n"; 34 } 35 36 void T::adjust(int ratio) { 37 m1 *= ratio; 38 m2 *= ratio; 39 } 40 41 void T::display() const { 42 std::cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ; 43 } 44 45 int T::get_cnt() 46 { 47 return cnt; 48 } 49 // 普通函数实现 50 void func() { 51 T t5(42); 52 t5.m2 = 2049; 53 std::cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); std::cout << '\n'; 54 }

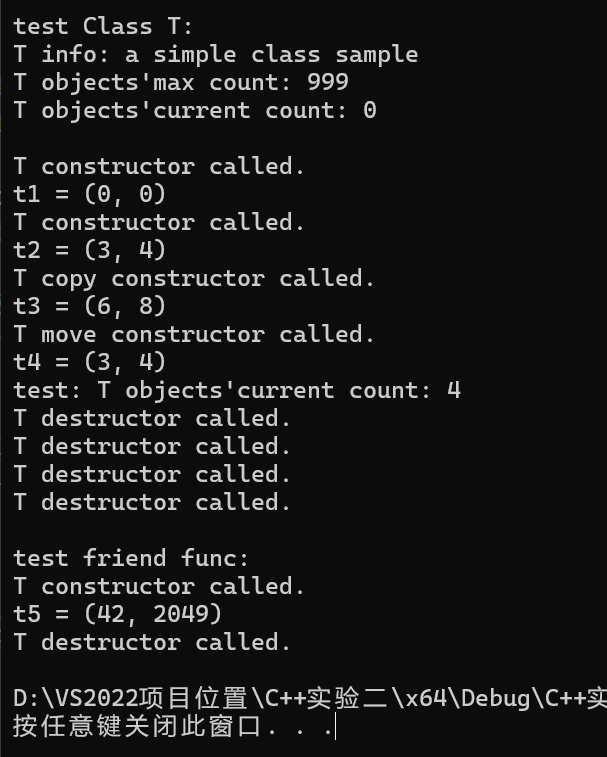
1 #include "T.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 void test_T(); 5 6 int main() { 7 std::cout << "test Class T: \n"; 8 test_T(); 9 10 std::cout << "\ntest friend func: \n"; 11 func(); 12 } 13 14 void test_T() { 15 using std::cout; 16 using std::endl; 17 18 cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl; 19 cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl; 20 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl; 21 22 T t1; 23 cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl; 24 25 T t2(3, 4); 26 cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl; 27 28 T t3(t2); 29 t3.adjust(2); 30 cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl; 31 32 T t4(std::move(t2)); 33 cout << "t4 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl; 34 35 cout << "test: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 36 }
1.问题1: T.h中,在类T内部,已声明 func 是T的友元函数。在类外部,去掉line36,重新编译,程序能否正常运行。 如果能,回答YES;如果不能,以截图形式提供编译报错信息,说明原因。
答:

(1)在注释后编译器丢出的警告让我给移动构造函数增加noexcept,这可能于编译器本身有关,因为移动构造函数本身是用来移动资源,操作过程中有出现问题的风险,而func作为T类的友元函数可能“干扰“”了编译器,让他检查的没有那么严格,所以注释前没报警告,注释后报了警告,但是无伤大雅,加上声明和定义出相应地方加上noexcept即可解决。
(2)在task.cpp文件中只包含了“T.h”头文件,如果不声明func函数,再task1.cpp文件中将找不到func函数,friend 友元声明的作用是给进行友元声明的函数相关的访问权限,不能替代函数的定义和声明。
问题2: T.h中,line9-12给出了各种构造函数、析构函数。总结它们各自的功能、调用时机。
答:line 9:
功能:普通的构造函数,并且设有默认值。给T类的对象进行初始化。
调用时机:初始化时只给0,1或2个int参数时由编译器自动调用。
line 10:
功能: 复制改造函数,通过一个已经存在的T类对象给一个新的T类对象初始化。
调用时机:初始化时给一个T类型的参数时由编译器自动调用。
line 11:
功能:移动构造函数,可以用一个T类型的右值给一个T类型的对象初始化。
调用时机:初始化时给一个T类型右值(比如一个临时对象,像函数返回的T类型的值,也可以用std::move()函数将一个T类的左值转换成右值)的参数时由编译器自动调用。
line 12:
功能:析构函数,当一个对象生命期到了后,负责执行一些扫尾工作,比如释放动态分配的内存。
调用时机:当一个对象的生命周期到了后,即即将被销毁前由编译器自动调用。
问题3: T.cpp中,line8-10,剪切到T.h的末尾,重新编译,程序能否正确编译。 如不能,以截图形式给出报错信息,分析原因。
答:
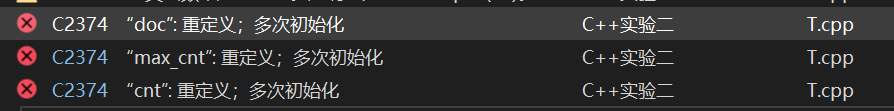
原因分析:在头文件中定义静态成员函数,而头文件被T.cpp和task1.cpp同时包含,而每个头文件是独立编译,这样这个const string doc ,const int max_cnt ,和int cnt三个静态成员变量会变会被编译两次,也就是会定义两次初始化两次,而他们实际上只需要定义初始化一次就够了,所以就会编译器就会报错“重定义,多次初始化”。
实验任务二:

1 #pragma once 2 #include<string> 3 4 class Complex 5 { 6 public: 7 static const std::string doc; 8 Complex(double _real = 0, double _imag = 0); 9 Complex(const Complex& other); 10 ~Complex(); 11 double get_real() const; 12 double get_imag() const; 13 void add(const Complex& t); 14 friend void output(const Complex& t); 15 friend double abs(const Complex& t); 16 friend Complex add(const Complex& m, const Complex& n); 17 friend bool is_equal(const Complex& m, const Complex& n); 18 friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex& m, const Complex& n); 19 20 private: 21 double real, imag; 22 }; 23 24 void output(const Complex& t); 25 double abs(const Complex& t); 26 Complex add(const Complex& m, const Complex& n); 27 bool is_equal(const Complex& m, const Complex& n); 28 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& m, const Complex& n);

1 #include"Complex.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cmath> 4 #include<iomanip> 5 const std::string Complex::doc = "a simplified complex class"; 6 Complex::Complex(double _real , double _imag ) 7 { 8 this->real = _real; 9 this->imag = _imag; 10 } 11 Complex::Complex(const Complex& other) 12 { 13 this->real = other.real; 14 this->imag = other.imag; 15 } 16 Complex::~Complex() {} 17 double Complex::get_real () const 18 { 19 return real; 20 } 21 double Complex::get_imag ()const 22 { 23 return imag; 24 } 25 void Complex::add(const Complex& t) 26 { 27 real += t.real; 28 imag += t.imag; 29 } 30 void output(const Complex& t) 31 { 32 std::cout << t.real << std::showpos << t.imag << 'i' << '\n'; 33 std::cout << std::noshowpos; 34 } 35 double abs(const Complex& t) 36 { 37 return sqrt(t.imag * t.imag + t.real * t.real); 38 } 39 Complex add(const Complex& m, const Complex& n) 40 { 41 return Complex(m.real + n.real, m.imag + n.imag); 42 } 43 bool is_equal(const Complex& m, const Complex& n) 44 { 45 if (m.real == n.real && m.imag == n.imag) 46 return true; 47 else return false; 48 } 49 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& m, const Complex& n) 50 { 51 if (is_equal(m, n)) 52 return false; 53 else 54 return true; 55 }

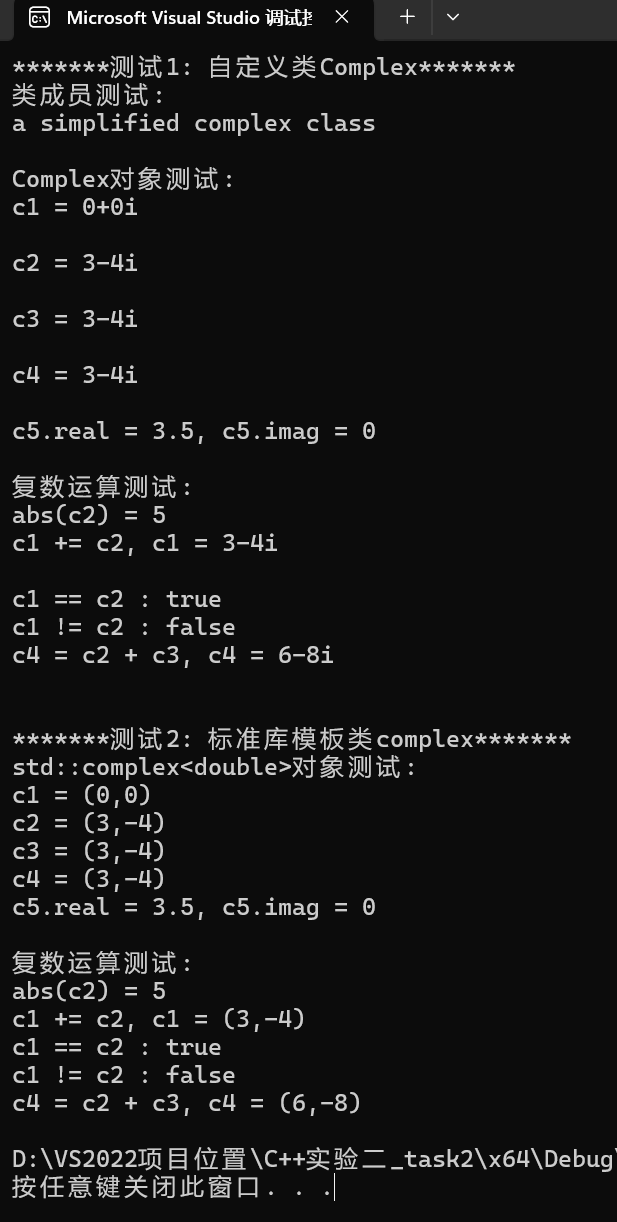
1 // 待补足头文件 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <iomanip> 4 #include <complex> 5 #include "D:/VS2022项目位置/C++实验二_task2/C++实验二_task2/Complex.h" 6 7 void test_Complex(); 8 void test_std_complex(); 9 10 int main() { 11 std::cout << "*******测试1: 自定义类Complex*******\n"; 12 test_Complex(); 13 14 std::cout << "\n*******测试2: 标准库模板类complex*******\n"; 15 test_std_complex(); 16 } 17 18 void test_Complex() { 19 using std::cout; 20 using std::endl; 21 using std::boolalpha; 22 23 cout << "类成员测试: " << endl; 24 cout << Complex::doc << endl << endl; 25 26 cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; 27 Complex c1; 28 Complex c2(3, -4); 29 Complex c3(c2); 30 Complex c4 = c2; 31 const Complex c5(3.5); 32 33 cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 34 cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; 35 cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; 36 cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 37 cout << "c5.real = " << c5.get_real() 38 << ", c5.imag = " << c5.get_imag() << endl << endl; 39 40 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 41 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 42 c1.add(c2); 43 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 44 cout << boolalpha; 45 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 46 cout << "c1 != c2 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 47 c4 = add(c2, c3); 48 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 49 } 50 51 void test_std_complex() { 52 using std::cout; 53 using std::endl; 54 using std::boolalpha; 55 56 cout << "std::complex<double>对象测试: " << endl; 57 std::complex<double> c1; 58 std::complex<double> c2(3, -4); 59 std::complex<double> c3(c2); 60 std::complex<double> c4 = c2; 61 const std::complex<double> c5(3.5); 62 63 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; 64 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; 65 cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; 66 cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; 67 68 cout << "c5.real = " << c5.real() 69 << ", c5.imag = " << c5.imag() << endl << endl; 70 71 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 72 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 73 c1 += c2; 74 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; 75 cout << boolalpha; 76 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2)<< endl; 77 cout << "c1 != c2 : " << (c1 != c2) << endl; 78 c4 = c2 + c3; 79 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; 80 }
问题1: 比较自定义类Complex和标准库模板类complex的用法,在使用形式上,哪一种更简洁?函数和运算内在有关 联吗?
答:(1)当然是标准模板库里的complex的用法更简洁,它重载了运算符来实现自定义类中用函数来实现的功能,明显操作符更简洁,可读性更高。
(2)有关联,其实运算符本身也是一种特殊的函数,只是它的调用形式更加简洁,本质的功能实现依旧是依靠函数
问题2: 2-1:自定义Complex中, output/abs/add/ 等均设为友元,它们真的需要访问 私有数据 吗?(回答“是/否”并 给出理由) 2-2:标准库 std::complex 是否把 abs 设为友元?(查阅 cppreference后回答) 2-3:什么时候才考虑使用 friend?总结你的思考。
答:(1)并不是,因为已经存在了接口get_real和get_imag,完全可以使用这两个接口来访问私有成员。
(2)并没有
(3)一种情况是当需要访问没有接口的私有成员变量时,另一种更典型的,可能性更多的情况是,需要调用类的私有成员和保护成员的函数时,将其声明为友元函数。
问题3: 如果构造对象时禁用=形式,即遇到Complex c4 = c2;编译报错,类Complex的设计应如何调整?
答:这时只需要把Complex的复制构造函数显示的删除就可以了,因为语句Complex c4 = c2;实际上还是再调用Complex的复制改造函数来完成初始化,只是这样一来Complex m(n);语句也会报错。
实验任务三:

#pragma once #include <string>enum class ControlType {Play, Pause, Next, Prev, Stop, Unknown};class PlayerControl { public:PlayerControl();ControlType parse(const std::string& control_str); // 实现std::string --> ControlType转换void execute(ControlType cmd) const; // 执行控制操作(以打印输出模拟) static int get_cnt();private:static int total_cnt; };

1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include<cstring> 5 int PlayerControl::total_cnt = 0; 6 7 PlayerControl::PlayerControl() {} 8 9 // 待补足 10 // 1. 将输入字符串转为小写,实现大小写不敏感 11 // 2. 匹配"play"/"pause"/"next"/"prev"/"stop"并返回对应枚举 12 // 3. 未匹配的字符串返回ControlType::Unknown 13 // 4. 每次成功调用parse时递增total_cnt 14 15 ControlType PlayerControl::parse(const std::string& control_str) { 16 std::string temp = control_str; 17 transform(control_str.begin(), control_str.end(), temp.begin(), tolower); 18 PlayerControl::total_cnt++; 19 if (temp == "play") 20 return ControlType::Play; 21 else if (temp == "pause") 22 return ControlType::Pause; 23 else if (temp == "next") 24 return ControlType::Next; 25 else if (temp == "prev") 26 return ControlType::Prev; 27 else if (temp == "stop") 28 return ControlType::Stop; 29 30 else 31 { 32 PlayerControl::total_cnt--; 33 return ControlType::Unknown; 34 } 35 } 36 37 void PlayerControl::execute(ControlType cmd) const { 38 switch (cmd) { 39 case ControlType::Play: std::cout << "[play] Playing music...\n"; break; 40 case ControlType::Pause: std::cout << "[Pause] Music paused\n"; break; 41 case ControlType::Next: std::cout << "[Next] Skipping to next track\n"; break; 42 case ControlType::Prev: std::cout << "[Prev] Back to previous track\n"; break; 43 case ControlType::Stop: std::cout << "[Stop] Music stopped\n"; break; 44 default: std::cout << "[Error] unknown control\n"; break; 45 } 46 } 47 48 int PlayerControl::get_cnt() { 49 return total_cnt; 50 }

#include "PlayerControl.h" #include <iostream>void test() {PlayerControl controller;std::string control_str;std::cout << "Enter Control: (play/pause/next/prev/stop/quit):\n";while(std::cin >> control_str) {if(control_str == "quit")break;ControlType cmd = controller.parse(control_str);controller.execute(cmd);std::cout << "Current Player control: " << PlayerControl::get_cnt() << "\n\n";} }int main() {test(); }
实验任务四:
分数的输出和计算, 由函数/类+static) output/add/sub/mul/div ,你选择的是哪一种设计方案?(友元/自由函数/命名空间+自 你的决策理由?如友元方案的优缺点、静态成员函数方案的适用场景、命名空间方案的考虑因素等。
答:我选择使用命名空间的方式。
考虑的因素:首先这些函数很多,如果声明成友元函数,友元函数很多,代码可读性下降,而且这么多友元函数不好管理而且也没有必要,这些函数的功能简单,使用类本身提供的接口完全可以实现相关的功能。 其次,静态成员函数+类的方式不放便函数的使用,每次都要加类名,使得代码冗长繁琐。使用命名空间可以解决前面的问题,即将这些相关度很大的函数封装再了一起,也可以通过using namespace XXX 的方式方便函数的调用。

1 #pragma once 2 #include<string> 3 4 class Fraction 5 { 6 public: 7 8 static const std::string doc; 9 10 Fraction(int up, int down = 1); 11 Fraction(const Fraction& other); 12 ~Fraction(); 13 14 int get_up() const; 15 int get_down() const; 16 Fraction negative(); 17 private: 18 19 int up; 20 int down; 21 }; 22 23 24 namespace Fraction_utility 25 { 26 void output(const Fraction& t); 27 Fraction add(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n); 28 Fraction sub(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n); 29 Fraction mul(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n); 30 Fraction div(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n); 31 Fraction div(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n); 32 33 };

1 #include"Fraction.h" 2 #include<numeric> 3 #include<iostream> 4 //静态成员 5 const std::string Fraction::doc = "Fraction类 v 0.01版.\n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加 / 减 / 乘 / 除运算."; 6 7 //自定义普通函数 8 int gcd(int a, int b) 9 { 10 int temp; 11 do 12 { 13 temp = a % b; 14 a = b; 15 b = temp; 16 } while (b != 0); 17 return a; 18 } 19 20 //成员函数 21 Fraction::Fraction(int _up, int _down ) 22 { 23 if (_down == 0) 24 { 25 up = 0; 26 down = 0; 27 } 28 else { 29 up = _up / gcd(_up, _down); 30 down = _down / gcd(_up, _down); 31 if (down < 0) 32 { 33 down = -down; 34 up = -up; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction& other) 39 { 40 if (other.get_down() == 0) 41 { 42 up = 0; 43 down = 0; 44 } 45 else { 46 up = other.up / gcd(other.up, other.down); 47 down = other.down / gcd(other.up, other.down); 48 if (down < 0) 49 { 50 down = -down; 51 up = -up; 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 Fraction::~Fraction() 56 { 57 58 } 59 int Fraction::get_up()const 60 { 61 return up; 62 } 63 int Fraction::get_down()const 64 { 65 return down; 66 } 67 Fraction Fraction::negative() 68 { 69 return Fraction(-up,down); 70 } 71 //命名空间函数定义 72 void Fraction_utility::output(const Fraction& t) 73 { 74 if (t.get_down() == 0 ) 75 std::cout << "分母不能为0" << '\n'; 76 if (t.get_up() % t.get_down() == 0) 77 std::cout << t.get_up() / t.get_down() << '\n'; 78 else 79 std::cout << t.get_up() << '/' << t.get_down() << '\n'; 80 } 81 Fraction Fraction_utility::add(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n) 82 { 83 int p = m.get_up()*n.get_down() + n.get_up()*m.get_down(); 84 int q = m.get_down() * n.get_down(); 85 int Gcd = gcd(p, q); 86 return Fraction(p/Gcd,q/Gcd); 87 } 88 Fraction Fraction_utility::sub(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n) 89 { 90 int p = m.get_up() * n.get_down() - n.get_up() * m.get_down(); 91 int q = m.get_down() + n.get_down(); 92 int Gcd = gcd(p, q); 93 return Fraction(p / Gcd, q / Gcd); 94 } 95 Fraction Fraction_utility::mul(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n) 96 { 97 int p = m.get_up() * n.get_up(); 98 int q = m.get_down() * n.get_down(); 99 int Gcd = gcd(p, q); 100 return Fraction(p / Gcd, q / Gcd); 101 } 102 Fraction Fraction_utility::div(const Fraction& m, const Fraction& n) 103 { 104 if (m.get_up() == 0 || n.get_up() == 0 || m.get_down() == 0||n.get_up()==0) 105 { 106 return Fraction(0, 0); 107 } 108 else { 109 int p = m.get_up() * n.get_down(); 110 int q = m.get_down() * n.get_up(); 111 int Gcd = gcd(p, q); 112 return Fraction(p / Gcd, q / Gcd); 113 } 114 }

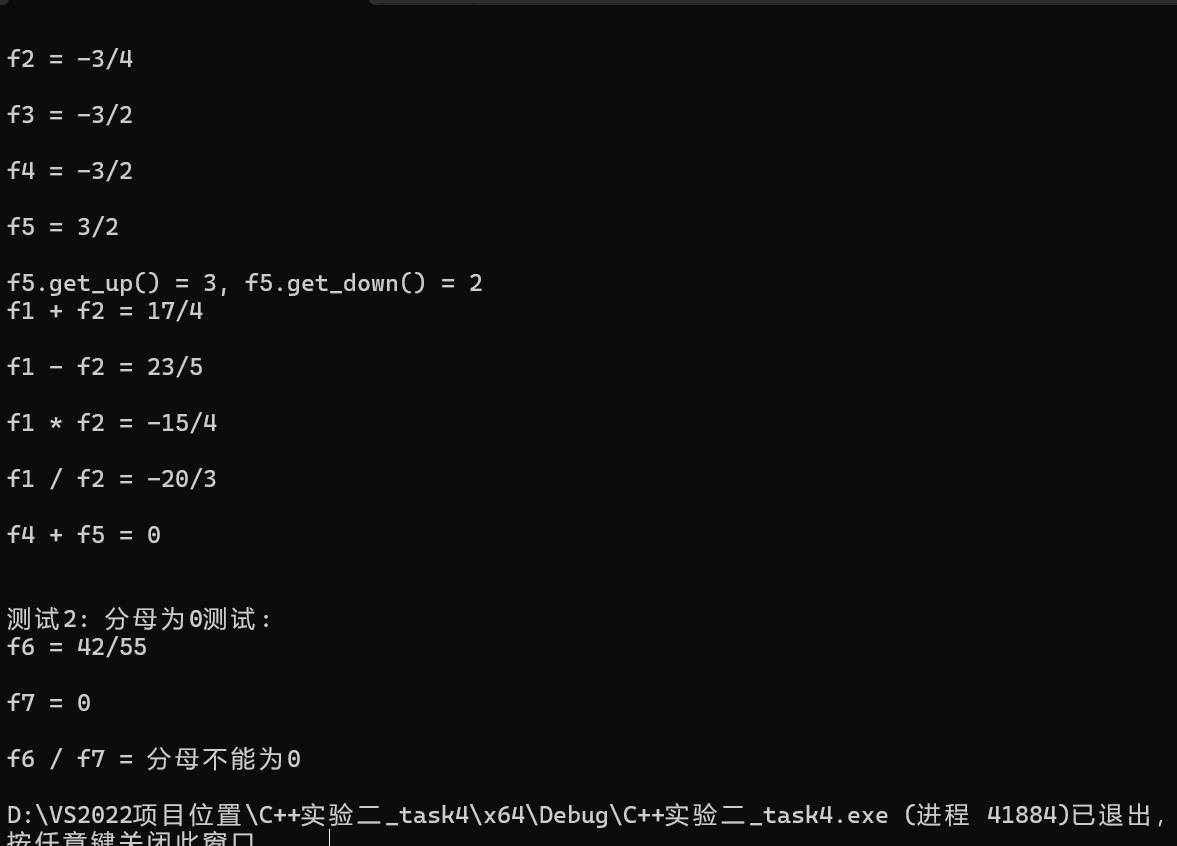
1 #include"D:\VS2022项目位置\C++实验二_task4\C++实验二_task4\Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace Fraction_utility; 4 void test1(); 5 void test2(); 6 7 8 int main() { 9 std::cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; 10 test1(); 11 12 std::cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; 13 test2(); 14 } 15 16 void test1() { 17 18 using std::cout; 19 using std::endl; 20 21 cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; 22 cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; 23 24 Fraction f1(5); 25 Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); 26 Fraction f4(f3); 27 cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; 28 cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; 29 cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; 30 cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; 31 32 const Fraction f5(f4.negative()); 33 cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; 34 cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() 35 << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; 36 37 cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 38 cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 39 cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 40 cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 41 cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; 42 } 43 44 void test2() { 45 using std::cout; 46 using std::endl; 47 48 Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); 49 cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; 50 cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; 51 cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; 52 }